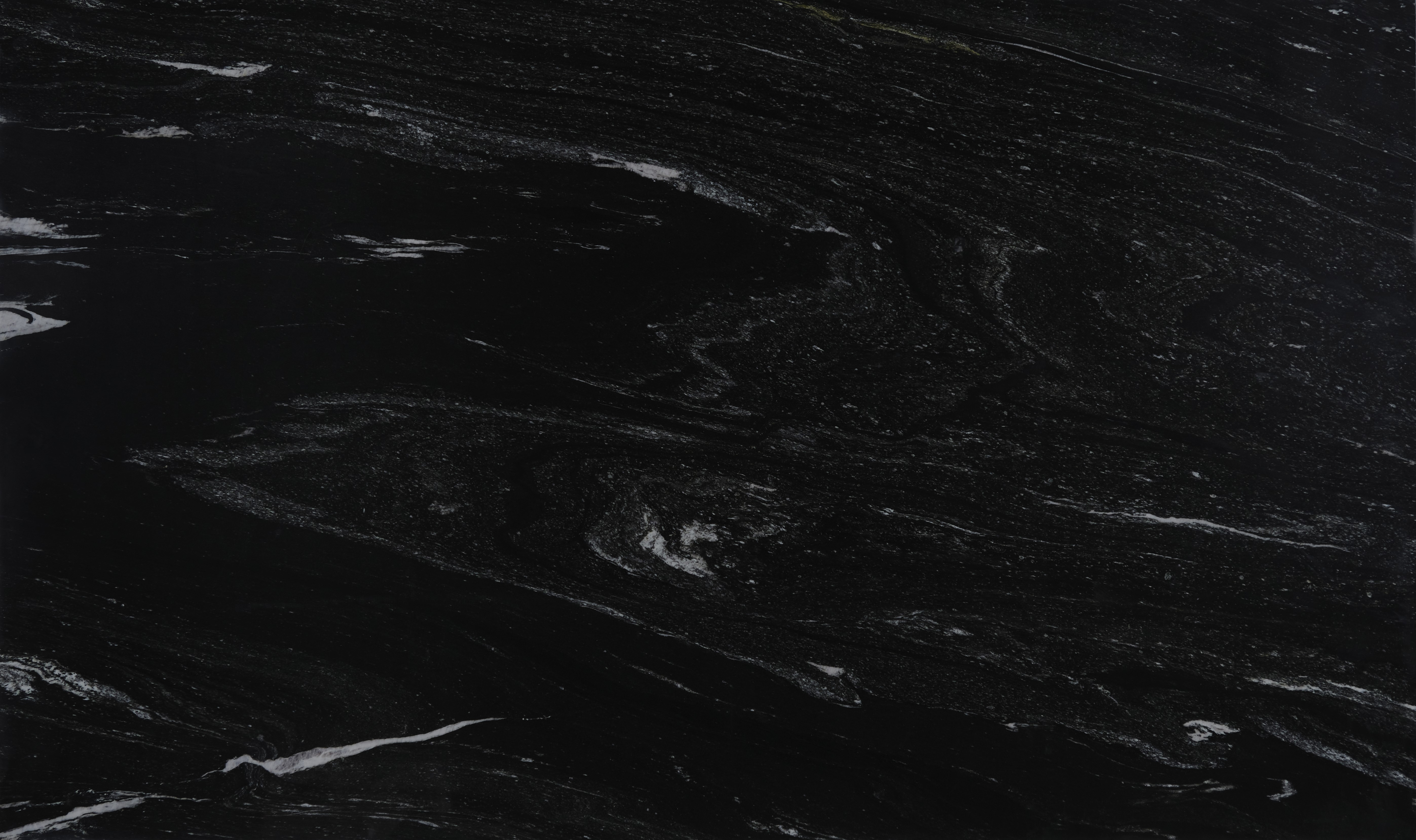
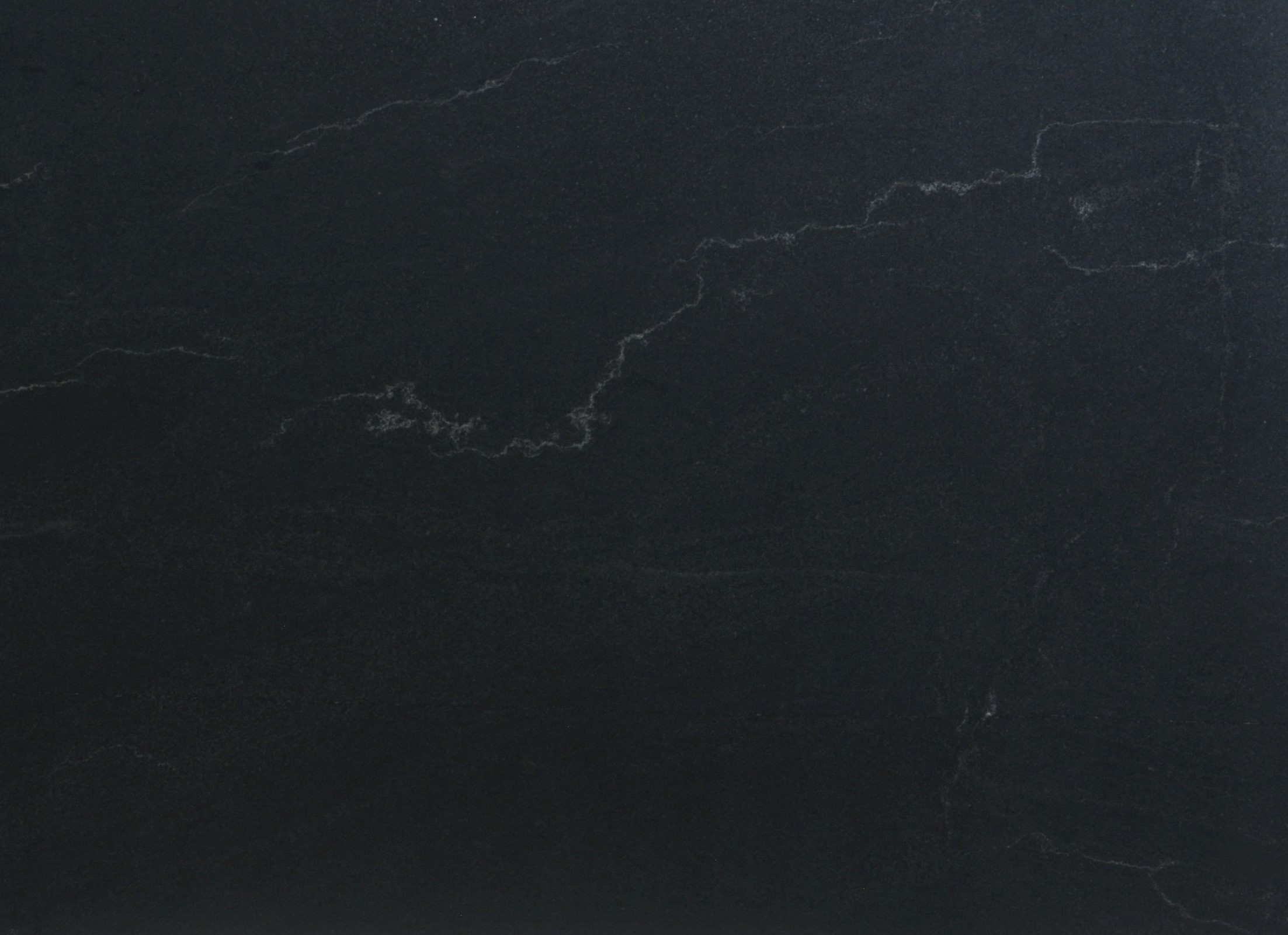
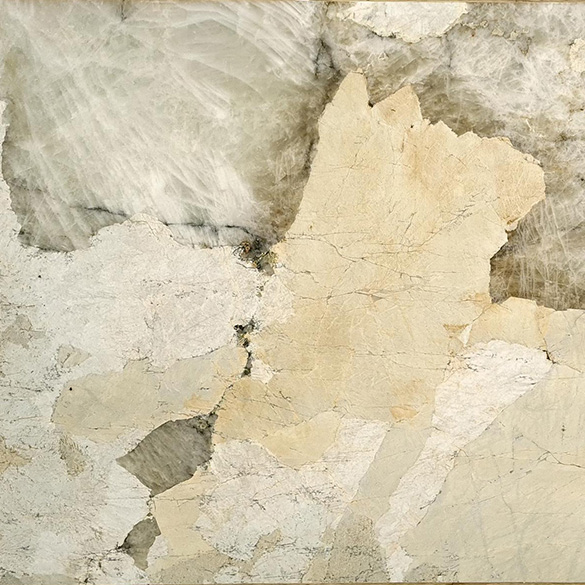
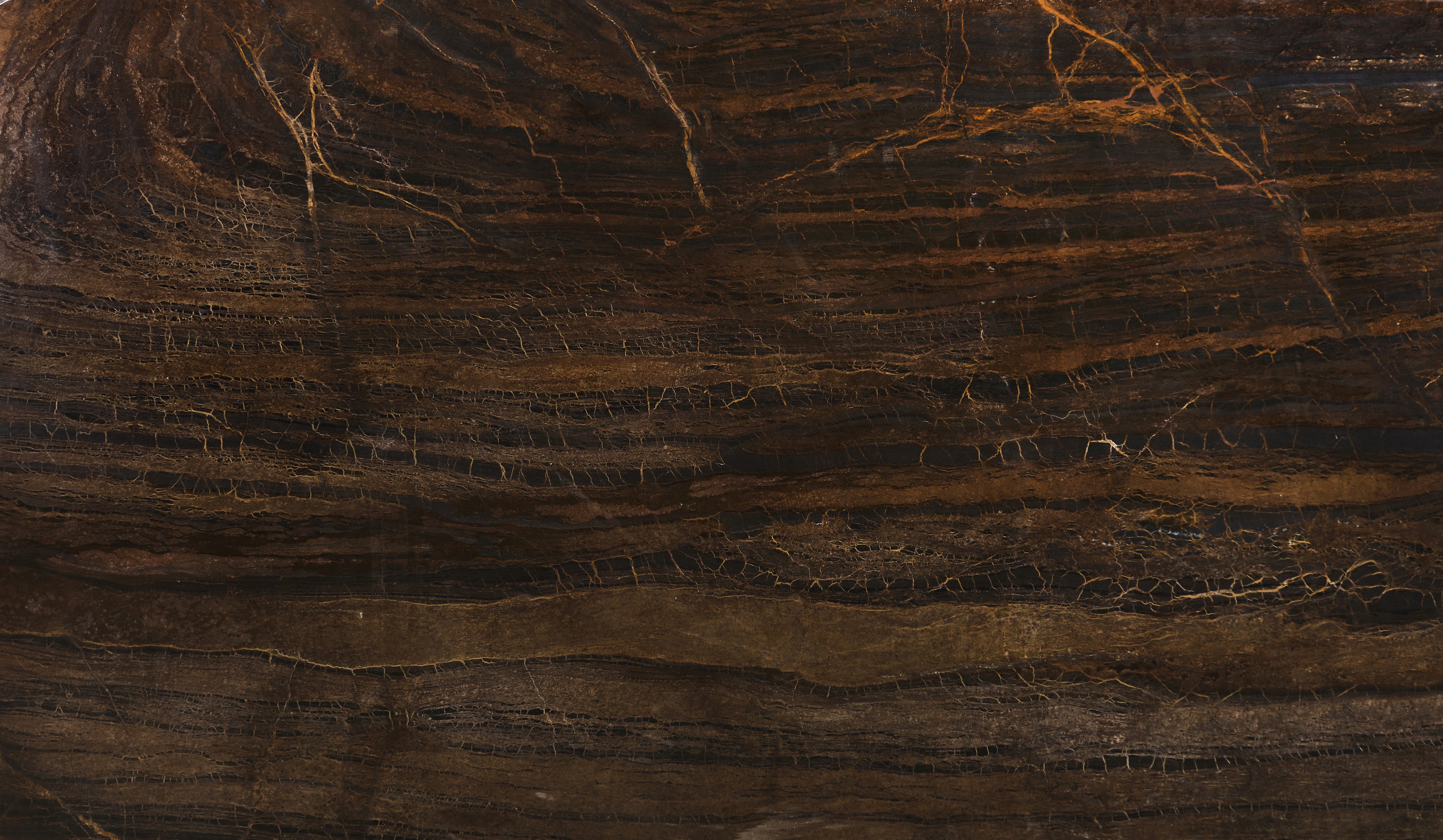
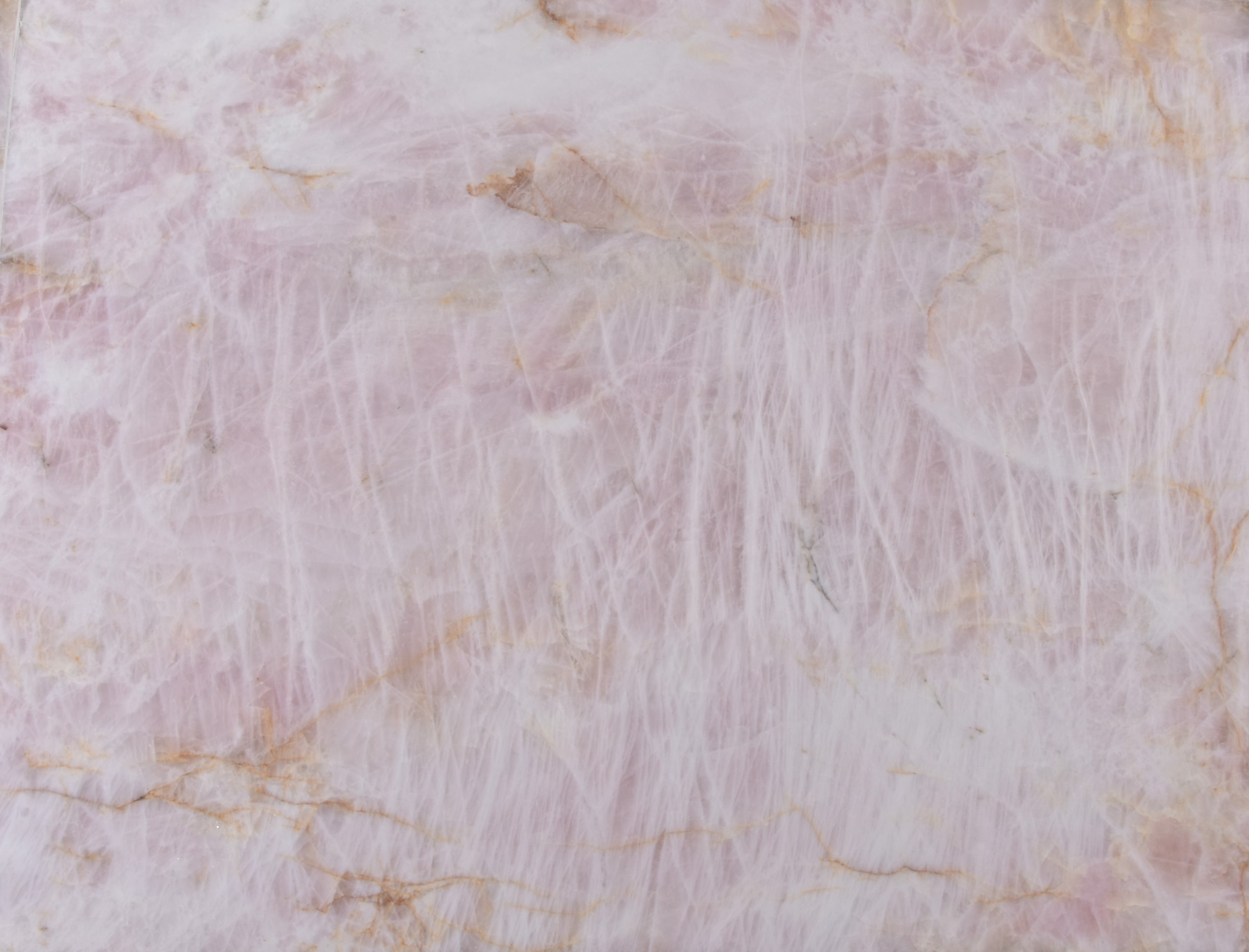
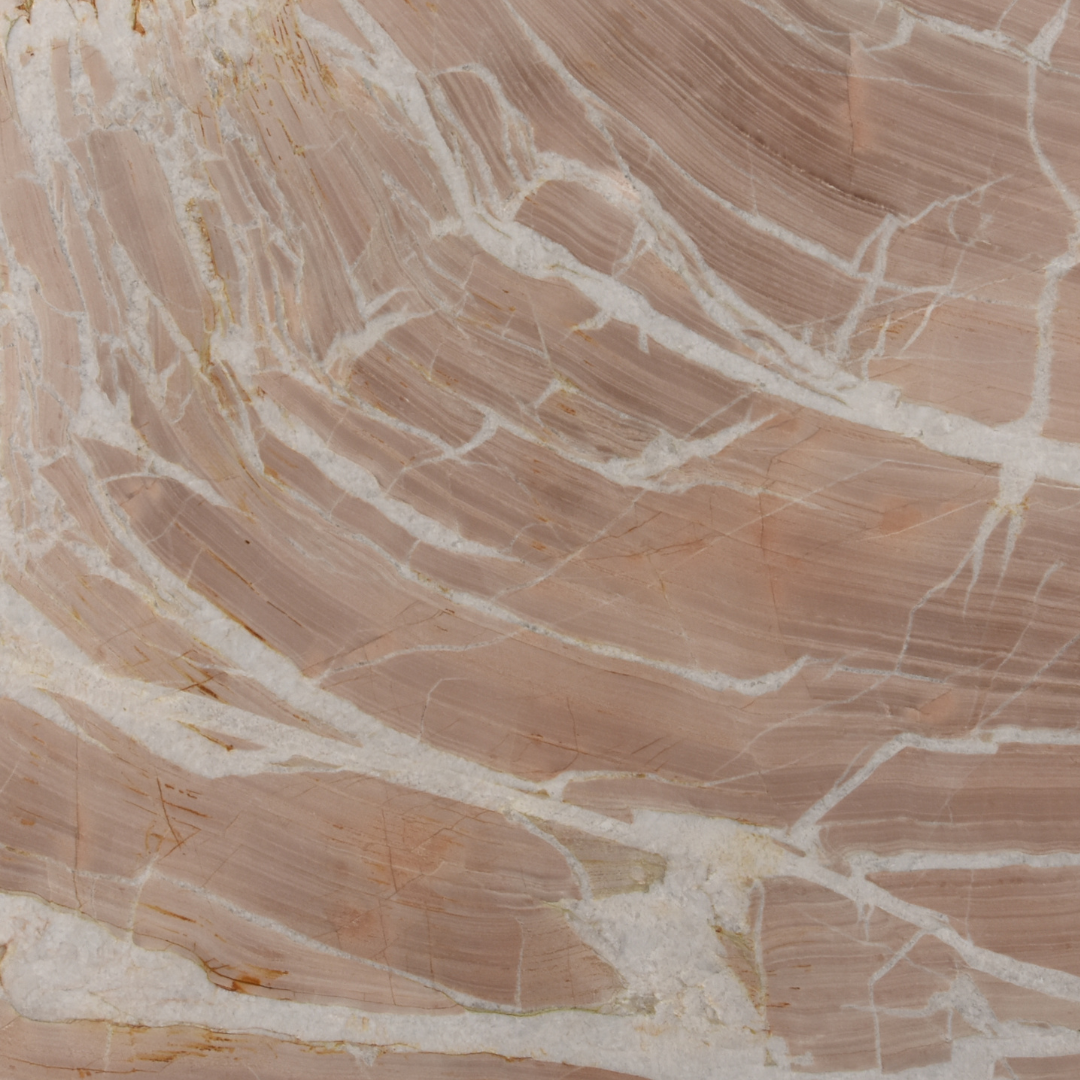
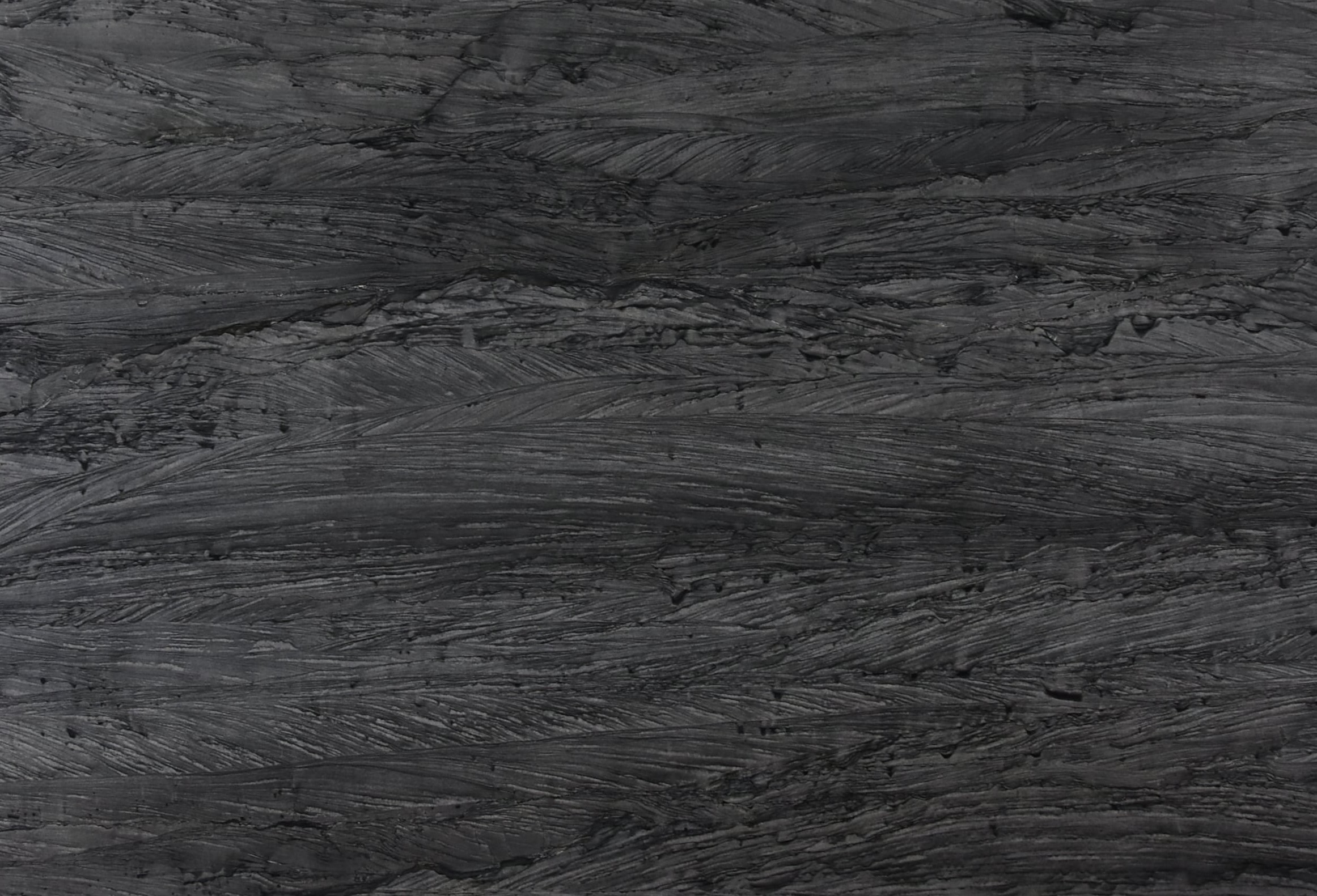
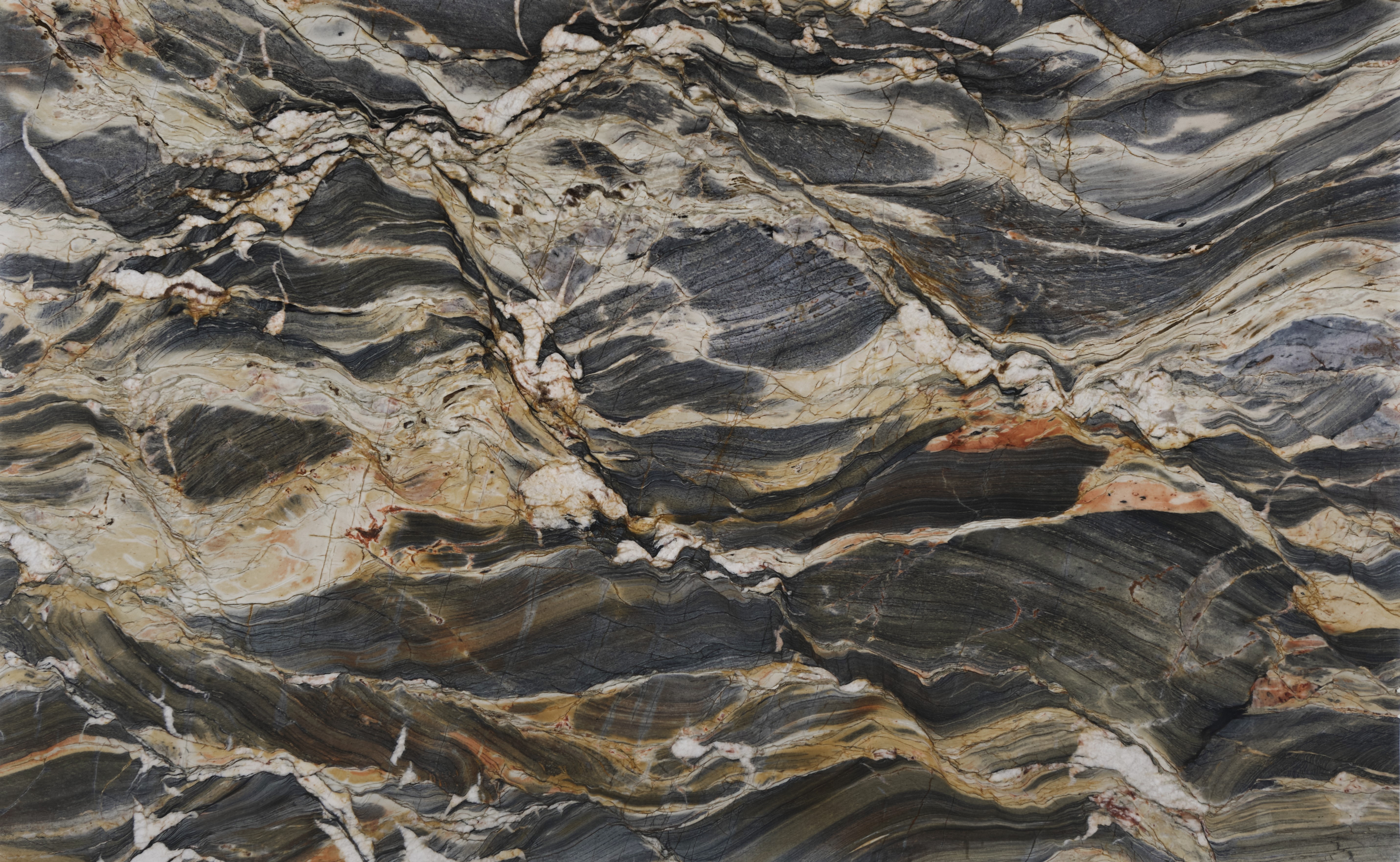
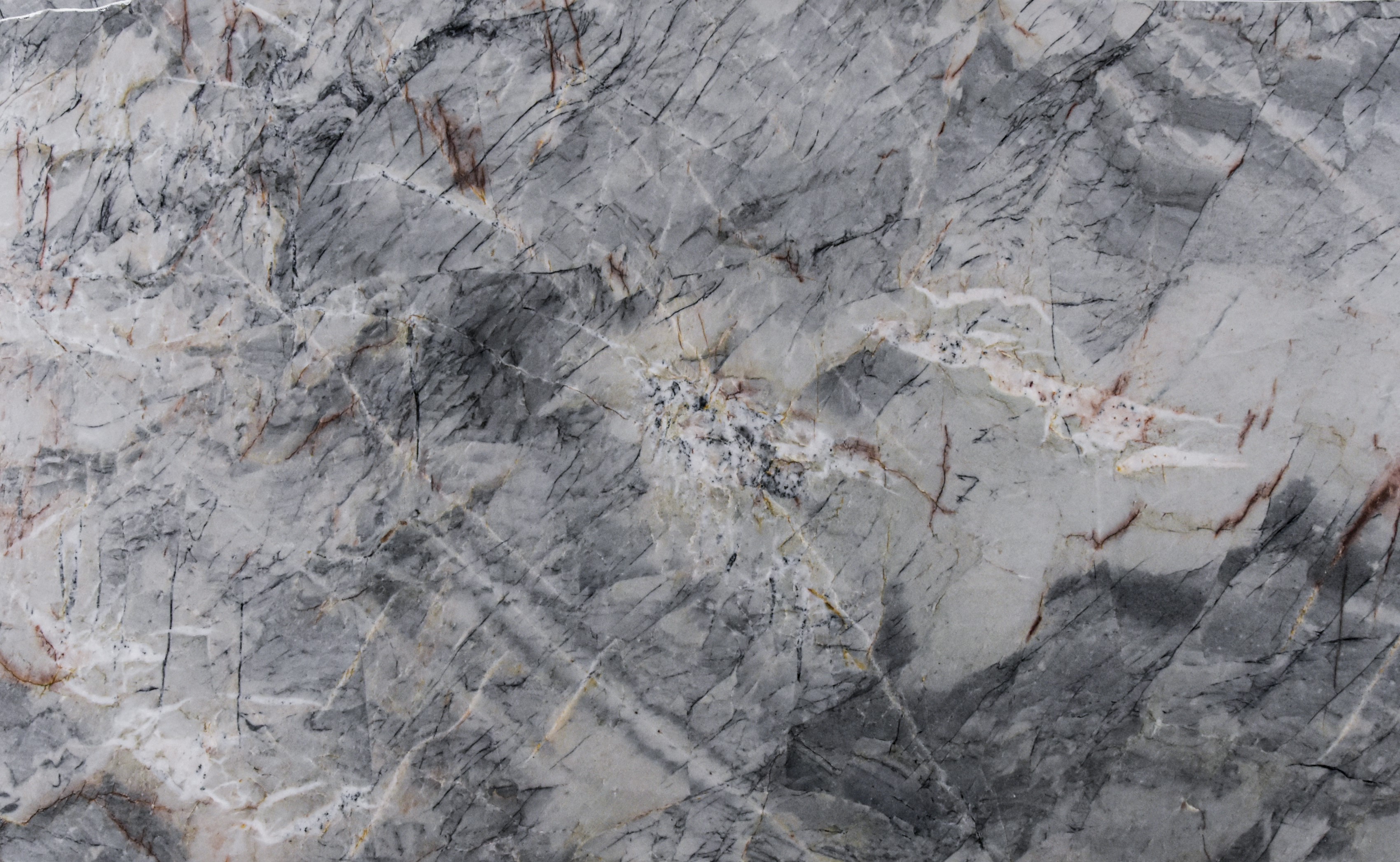
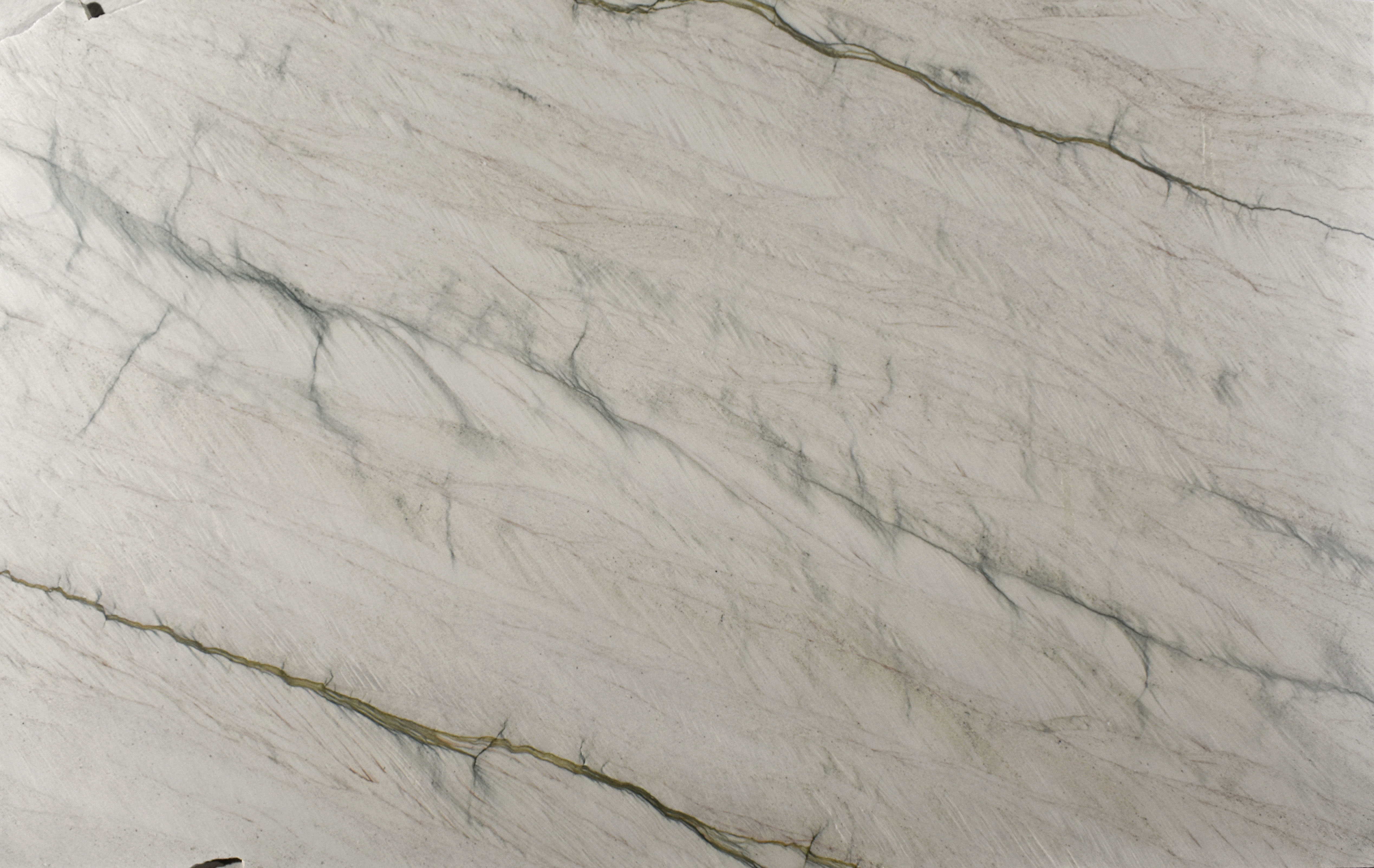
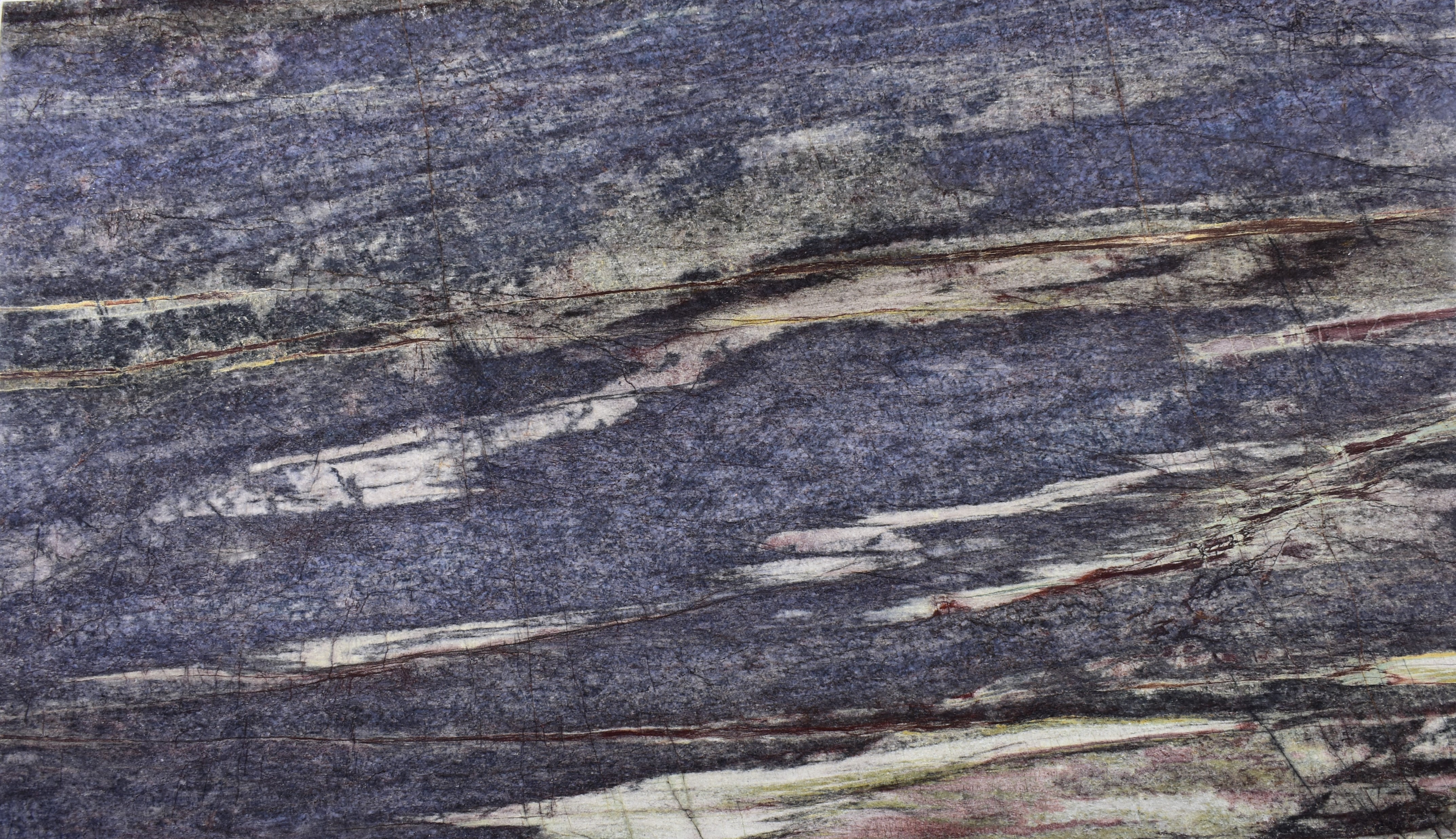
Quartzites
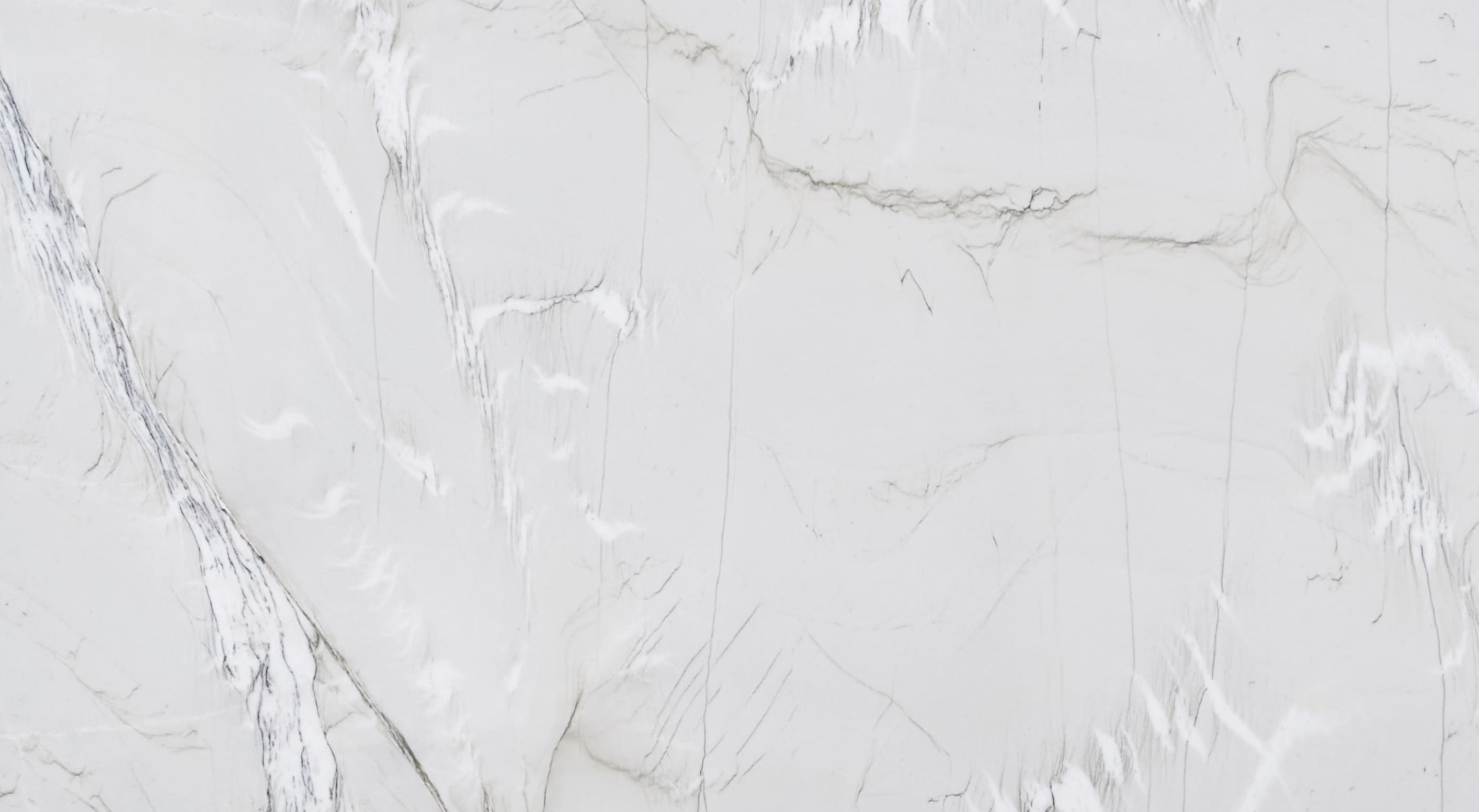
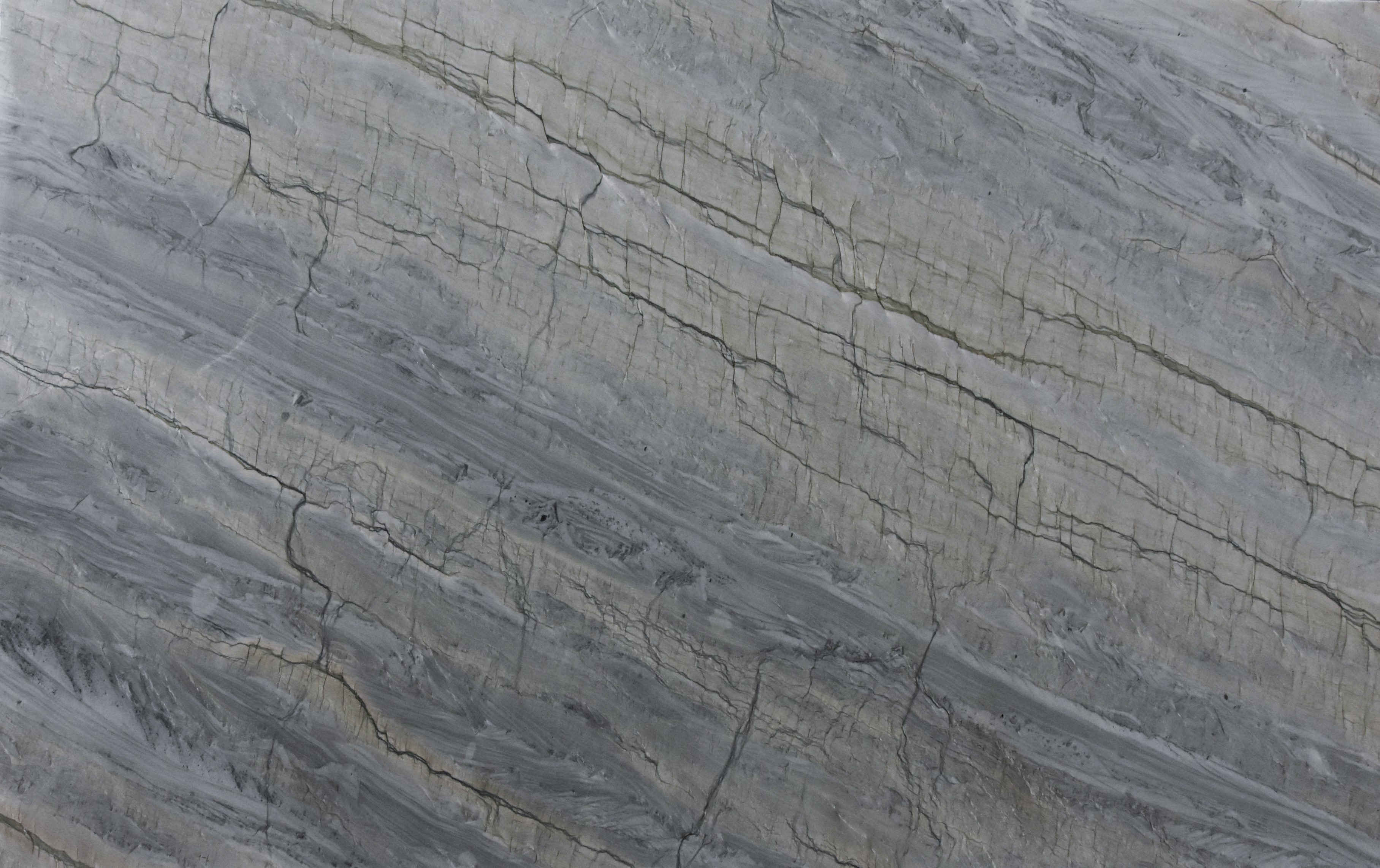
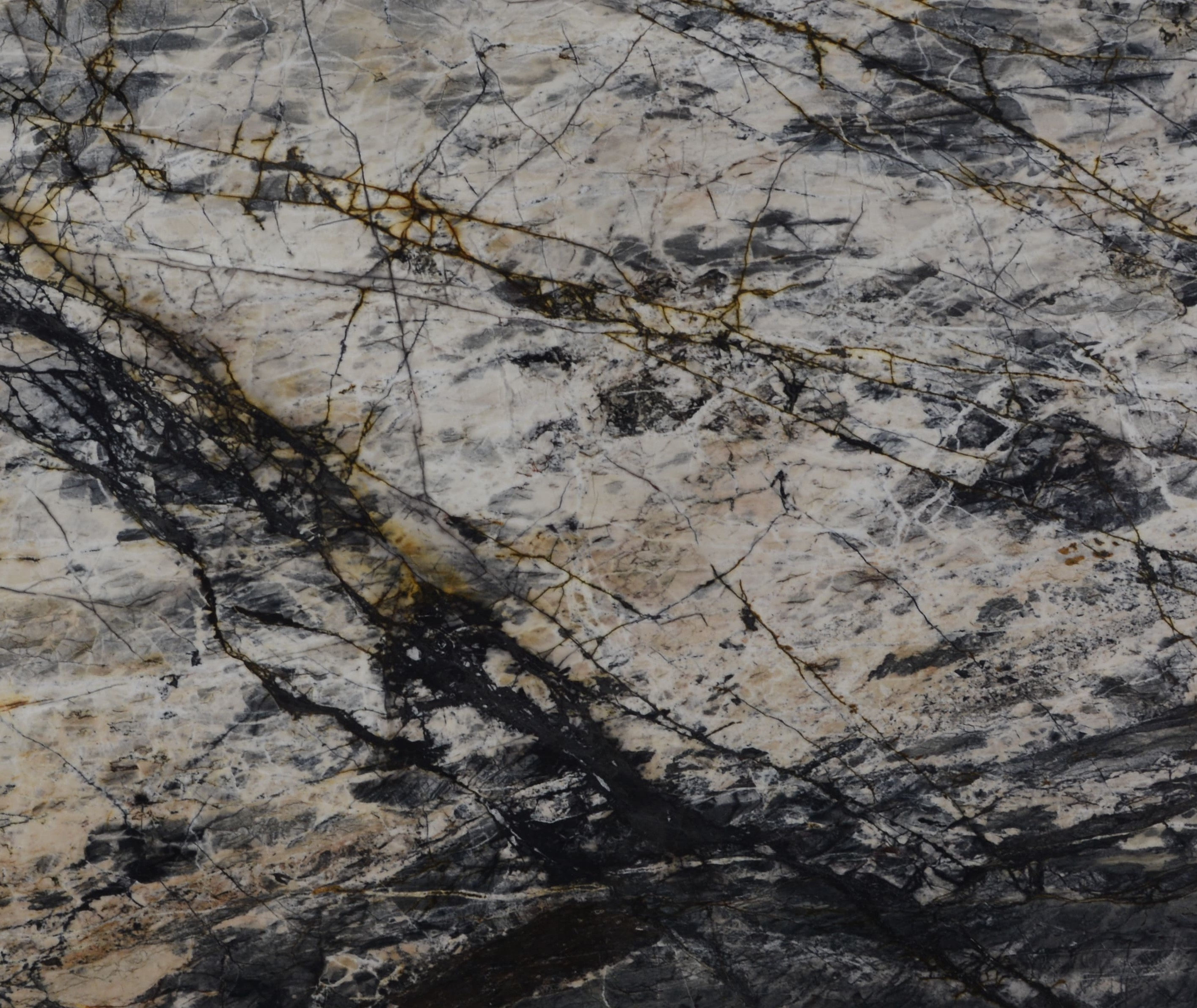
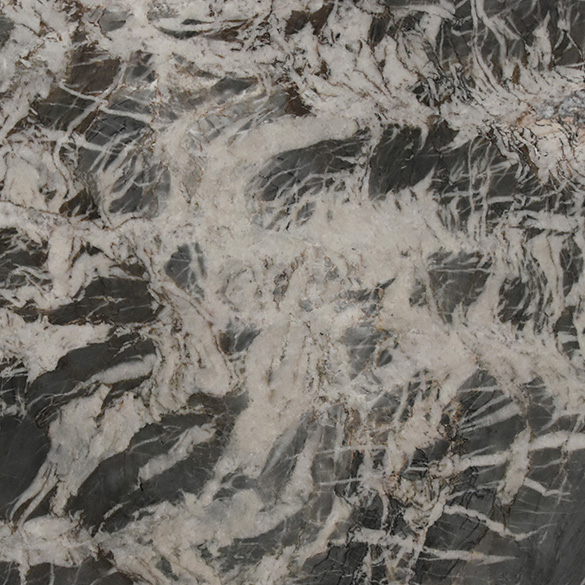
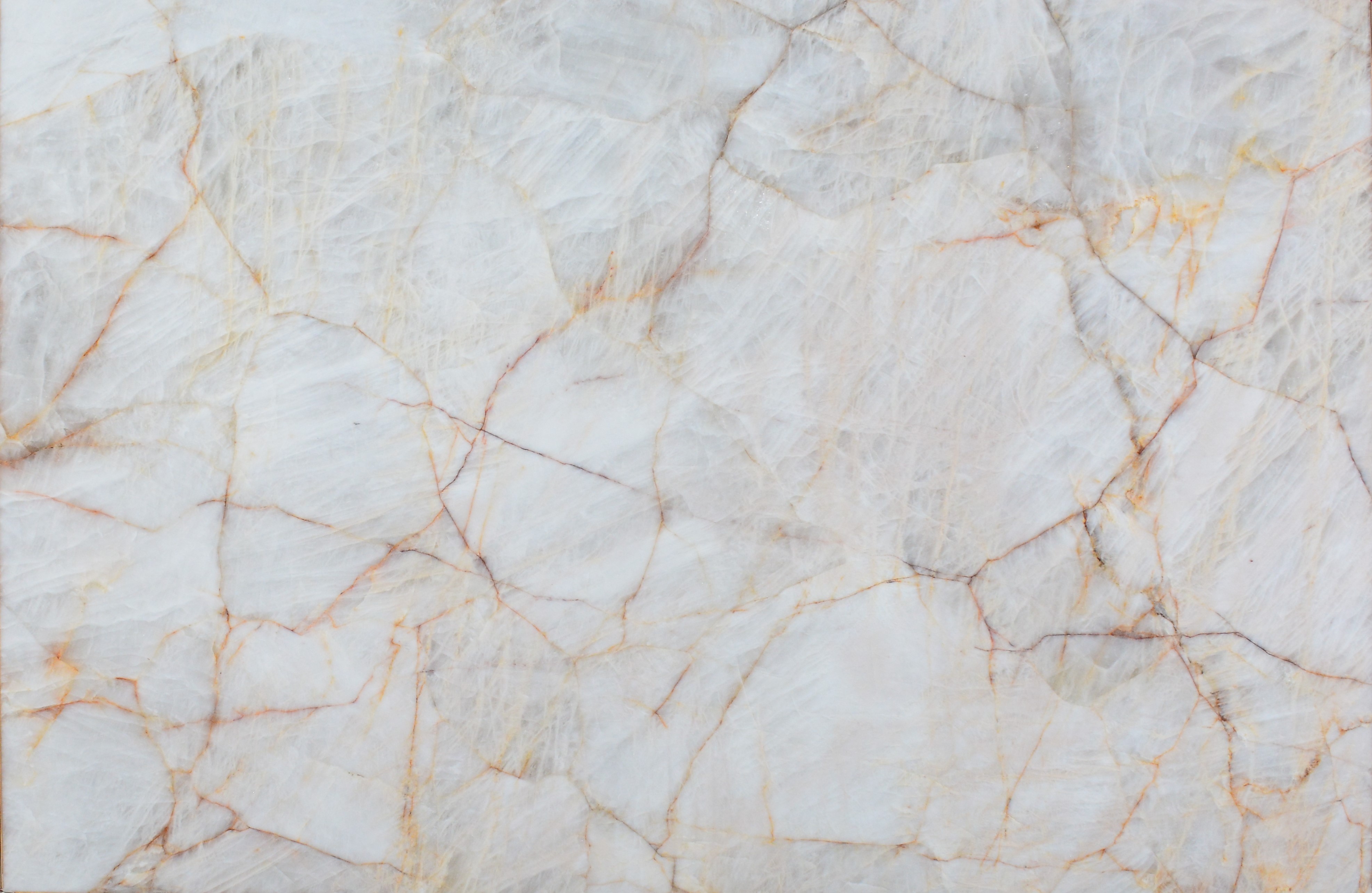
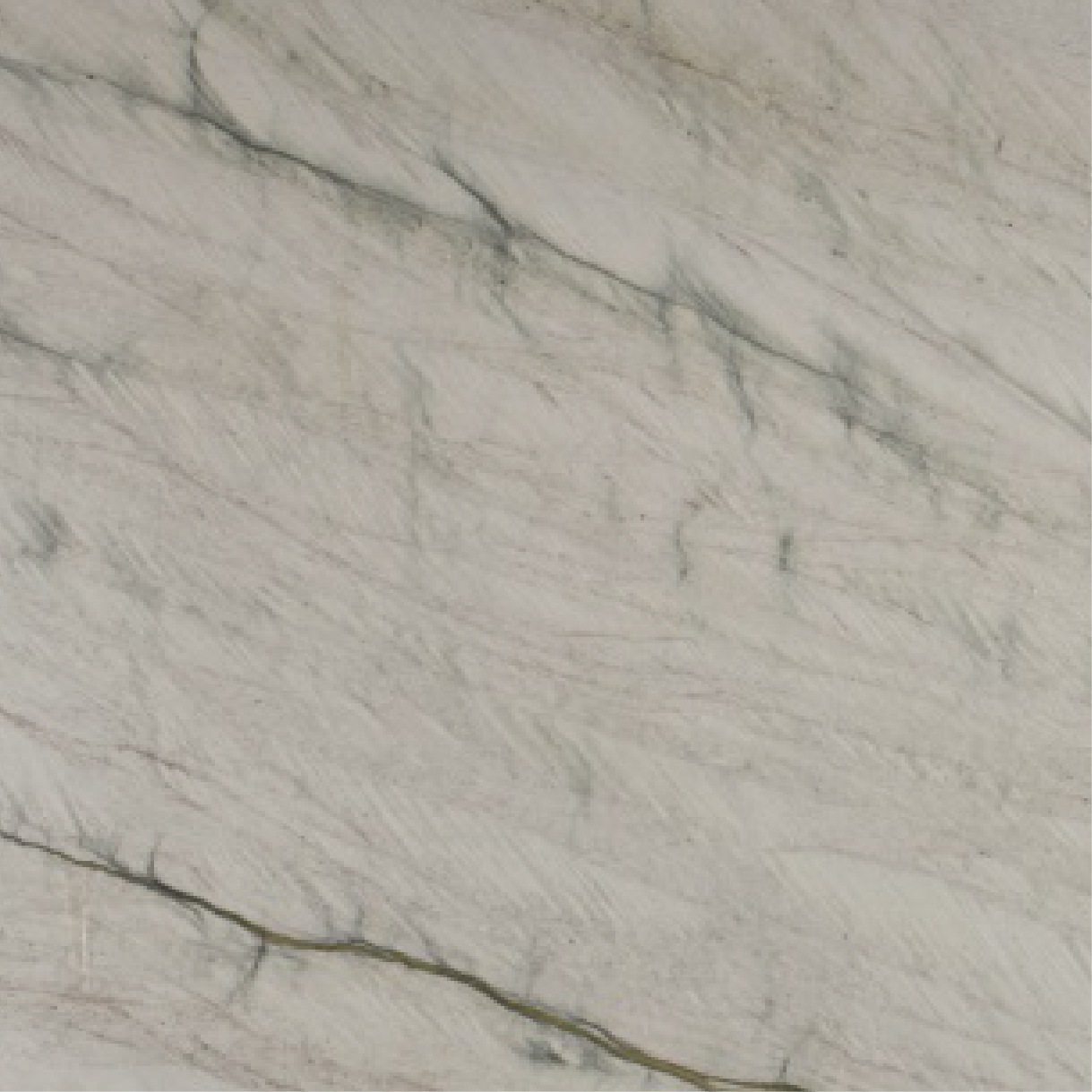
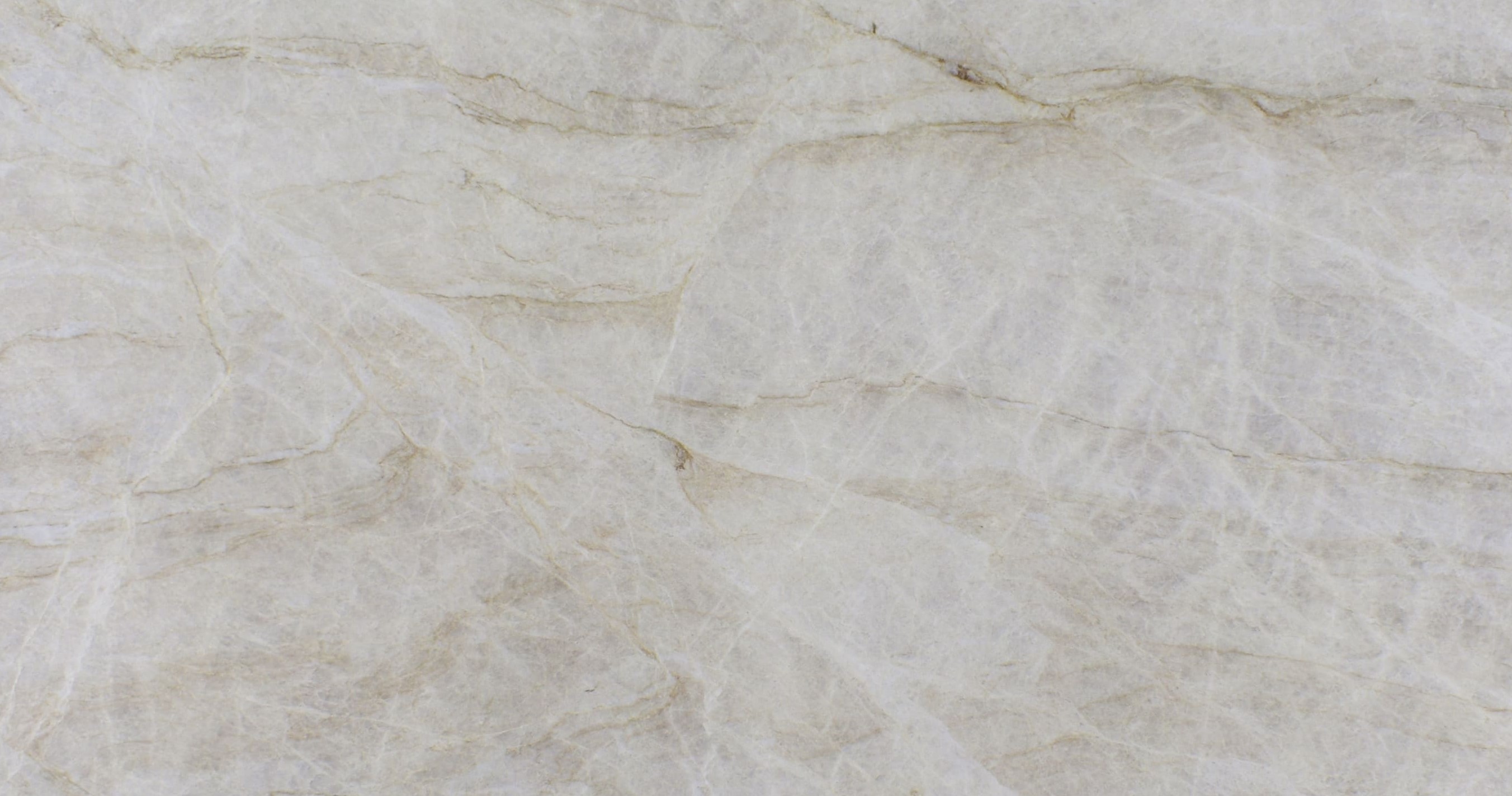
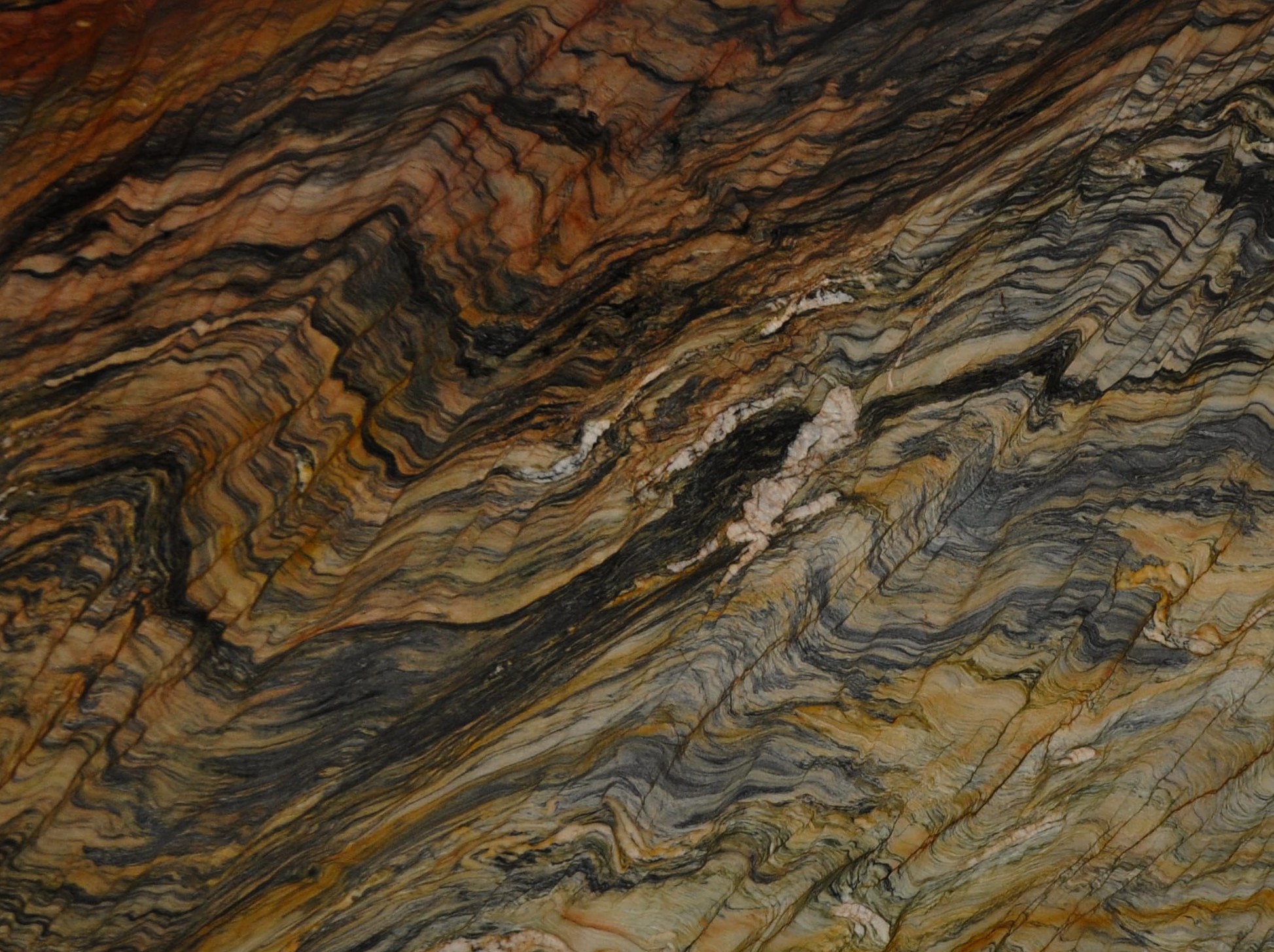
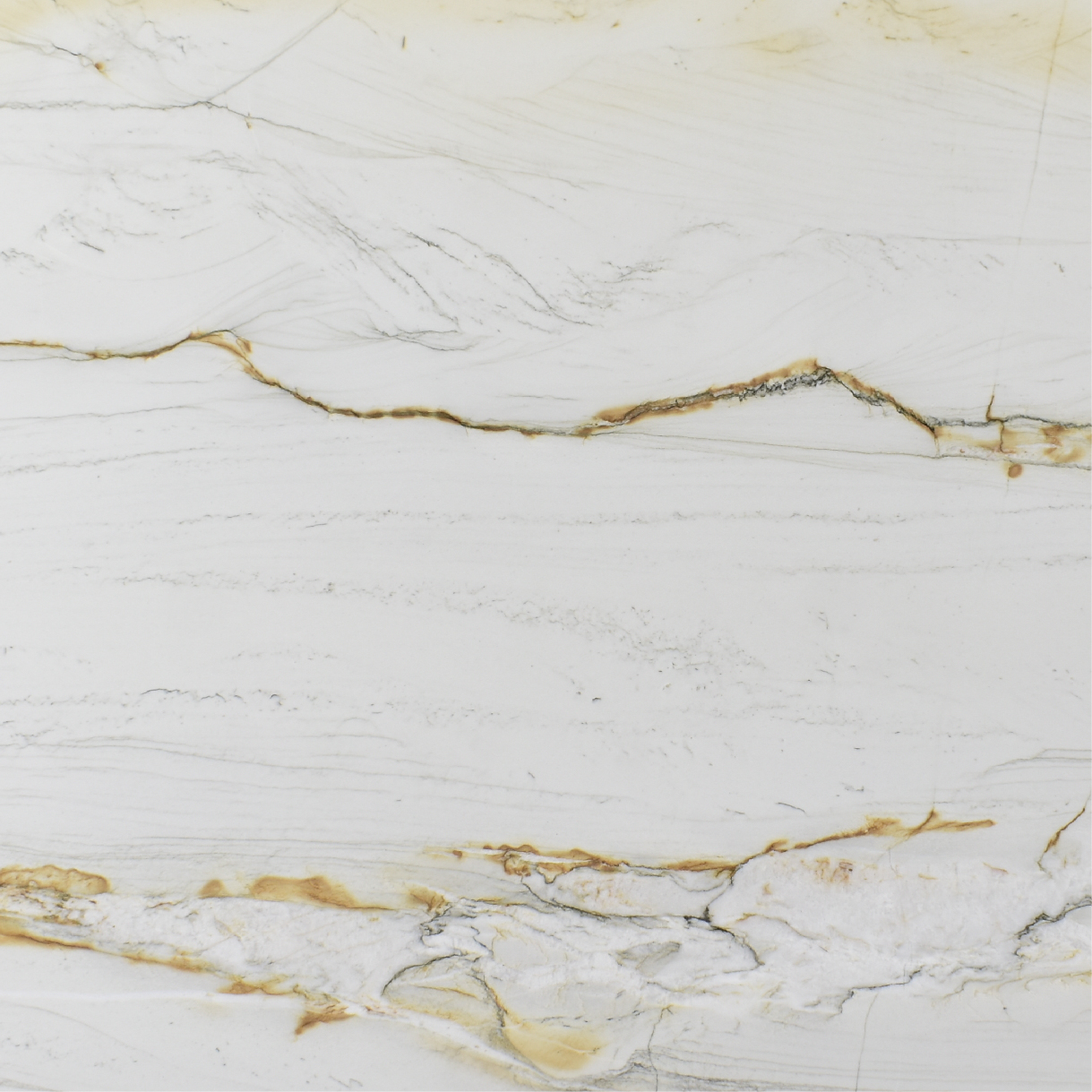
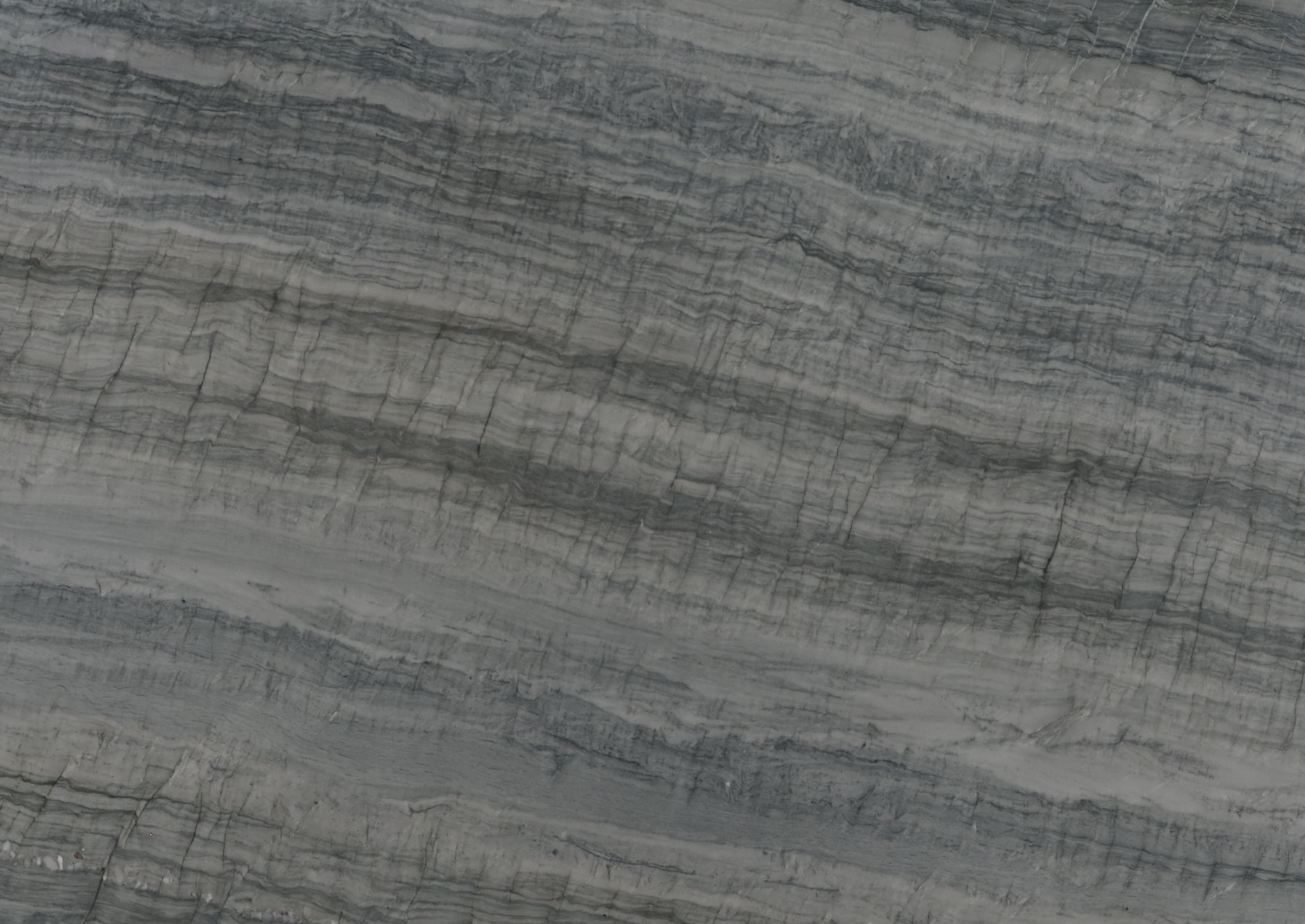
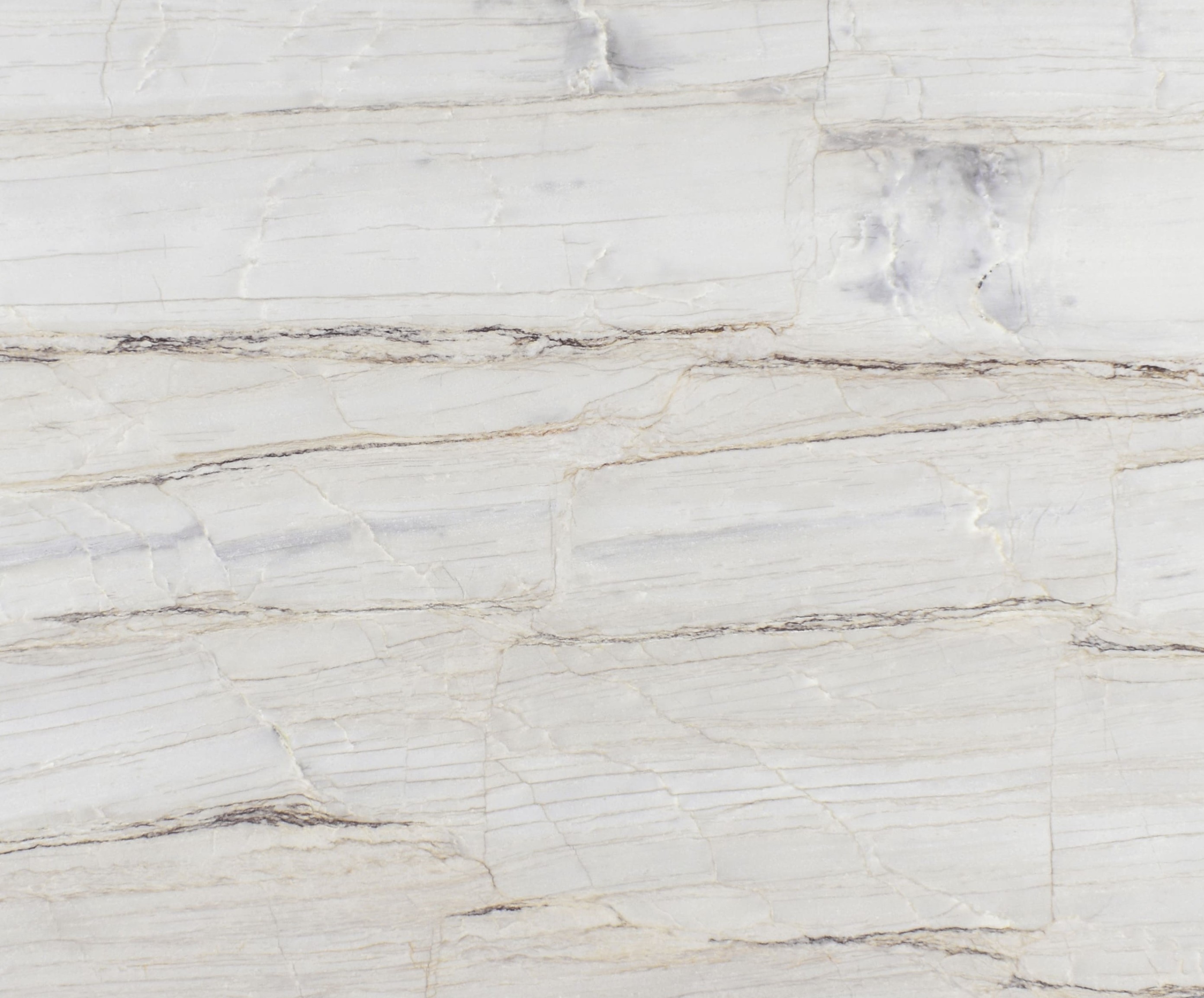
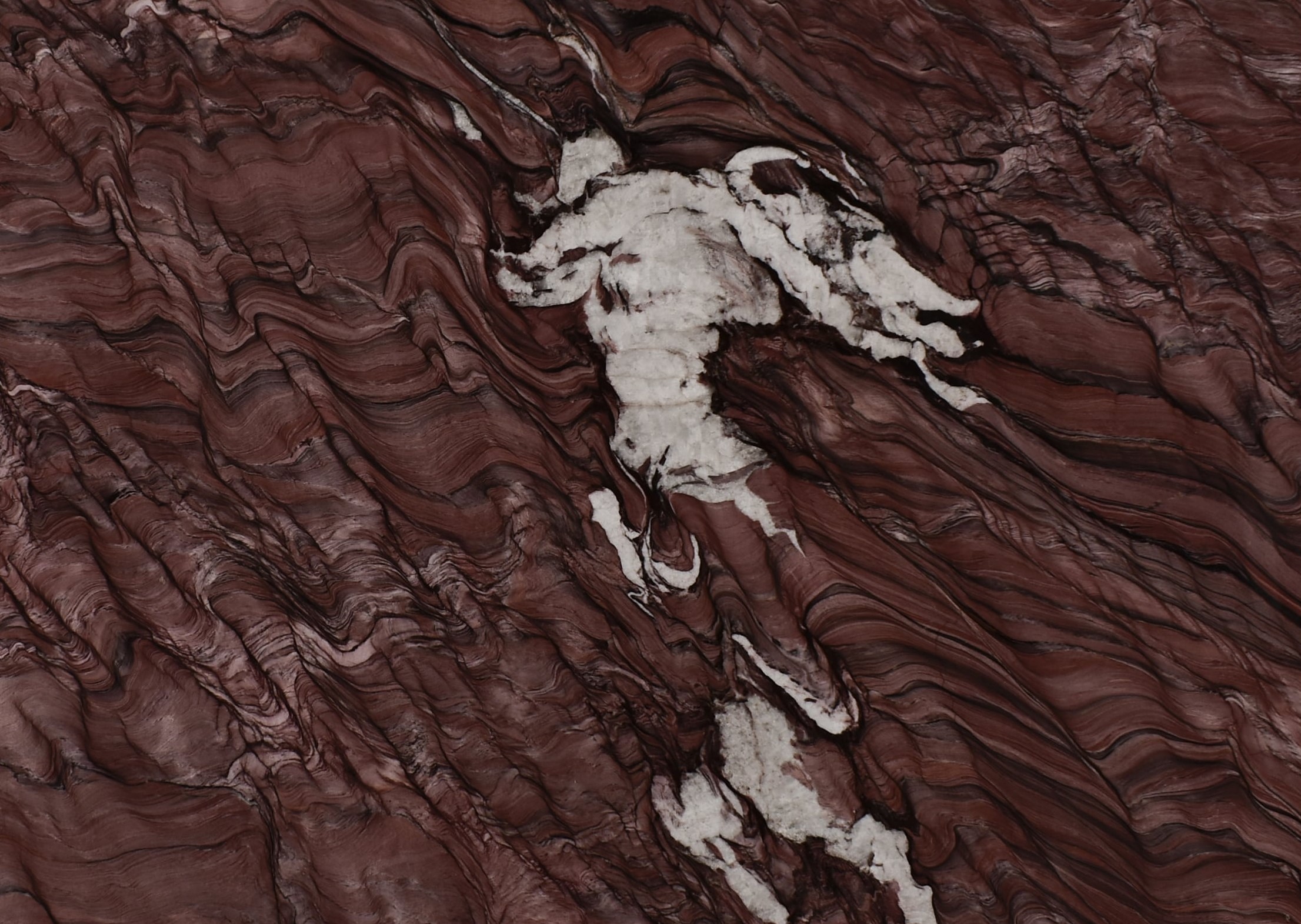
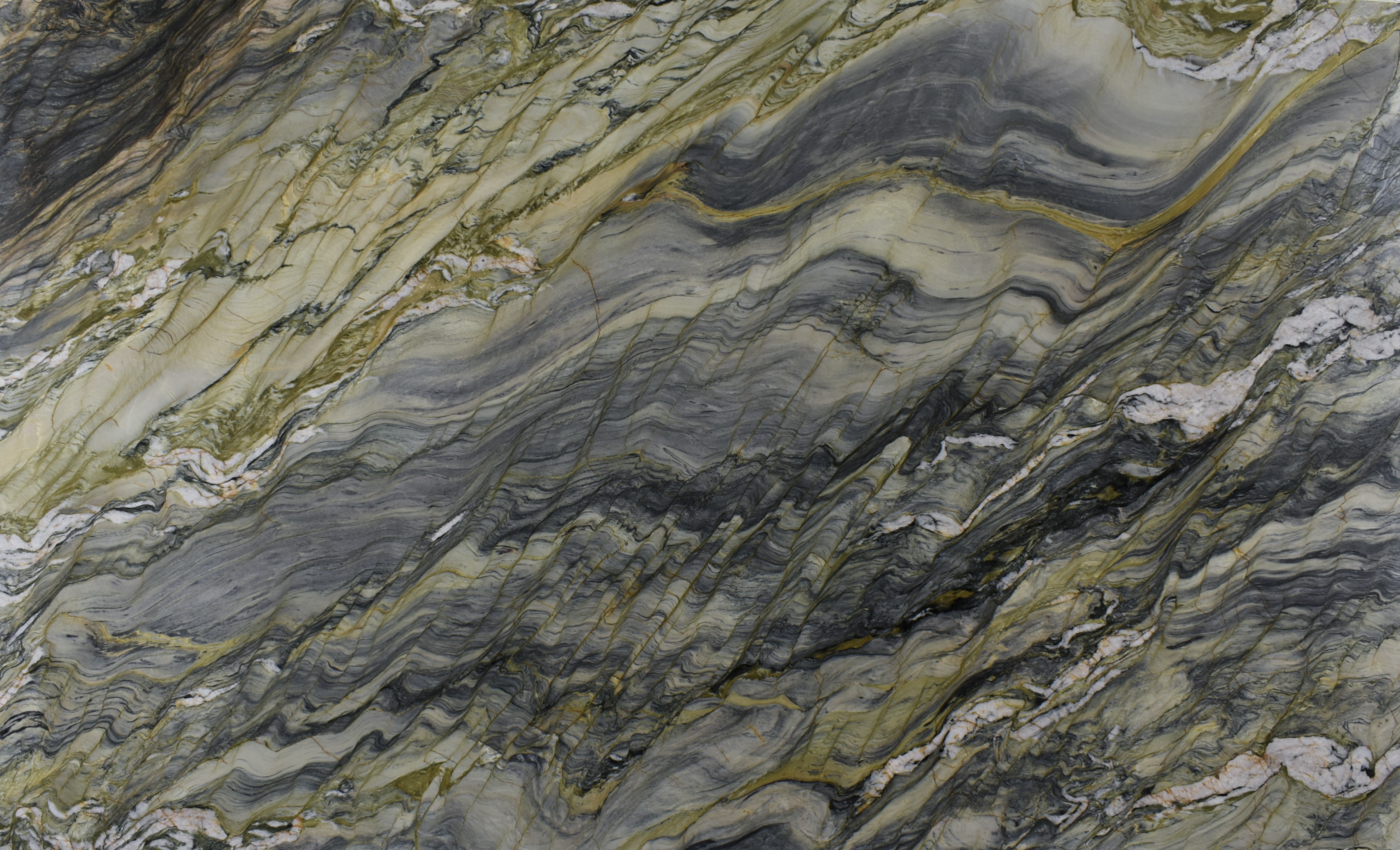
Meridian
The origin of the Meridian started in the Brazilian Northeast, 1.6 billion years ago, when the global climate change raised the sea level, removing continental sediments and producing quartz sand. Minerals such as dumortierite crystallized in the ocean water.
When these sediments accumulate in the sea, they are reworked by the tides. The uniqueness of Meridian quartz layers are traces of climate variation of its period of deposit, with sedimentary standards drawn by the ancient marine oscillation.
Finishes

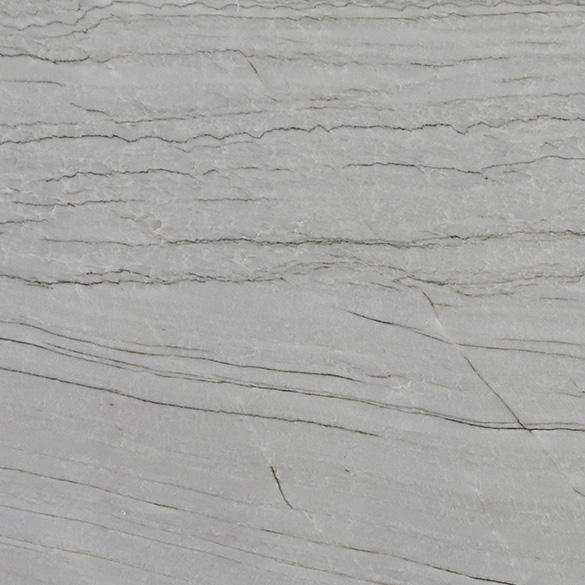
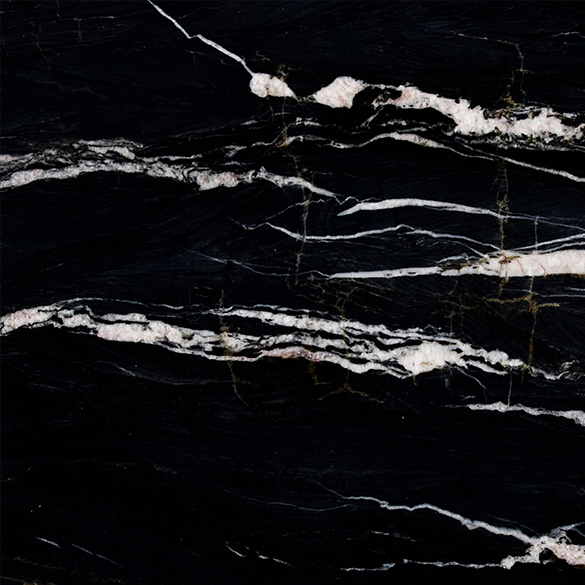
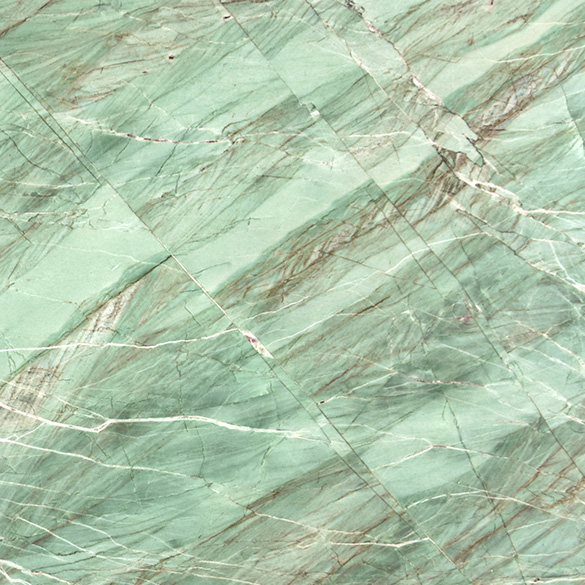
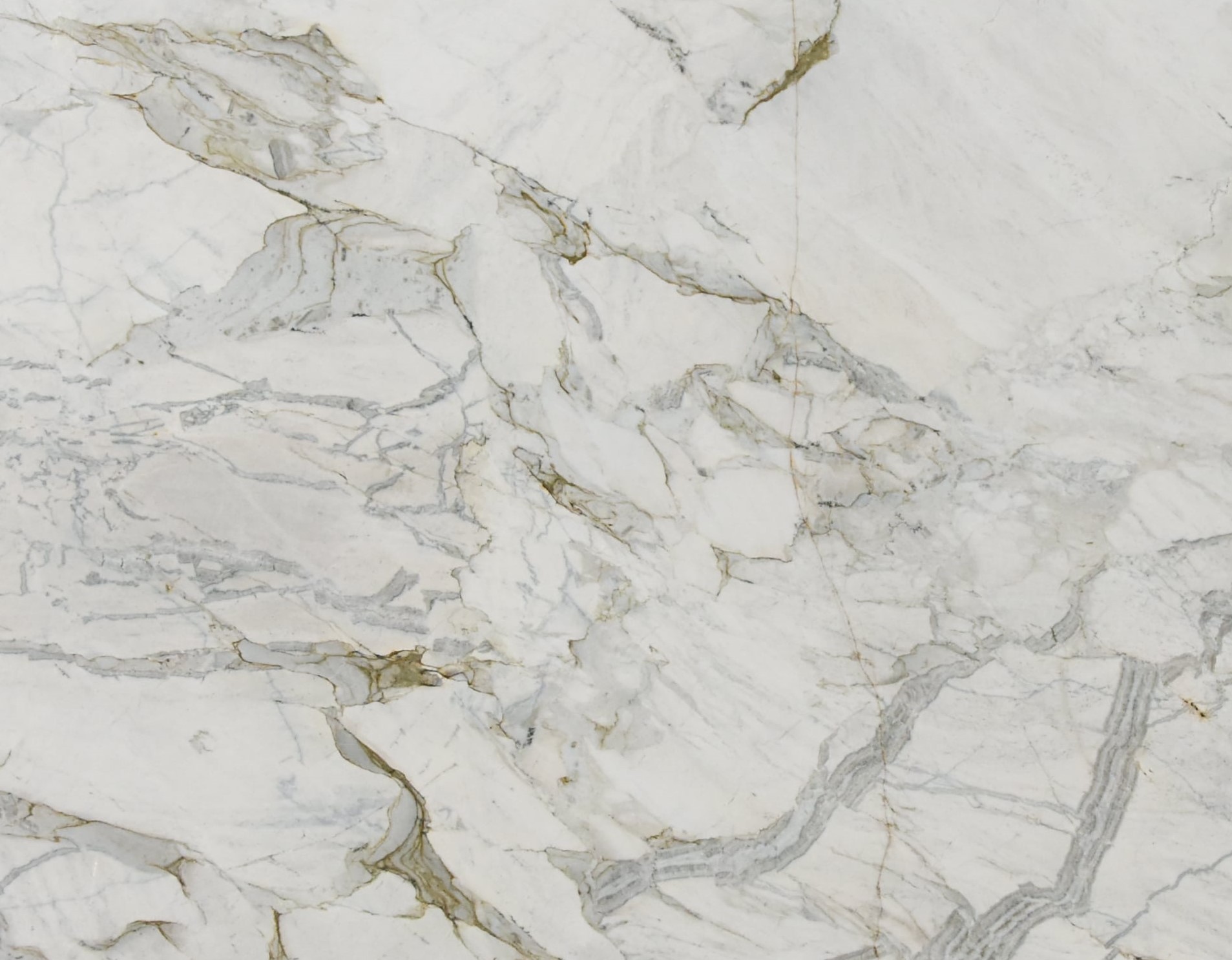
Polished
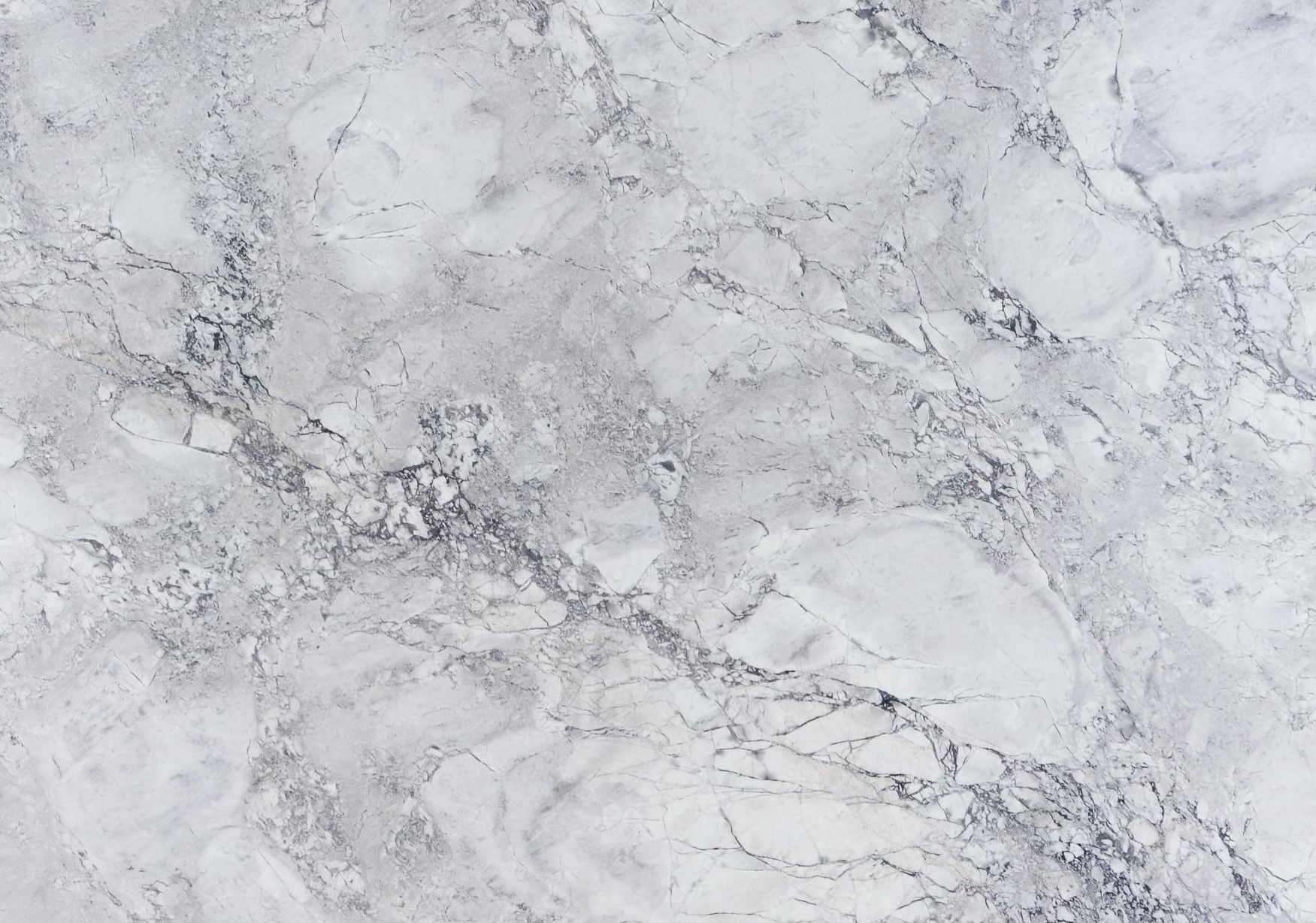
Brushed
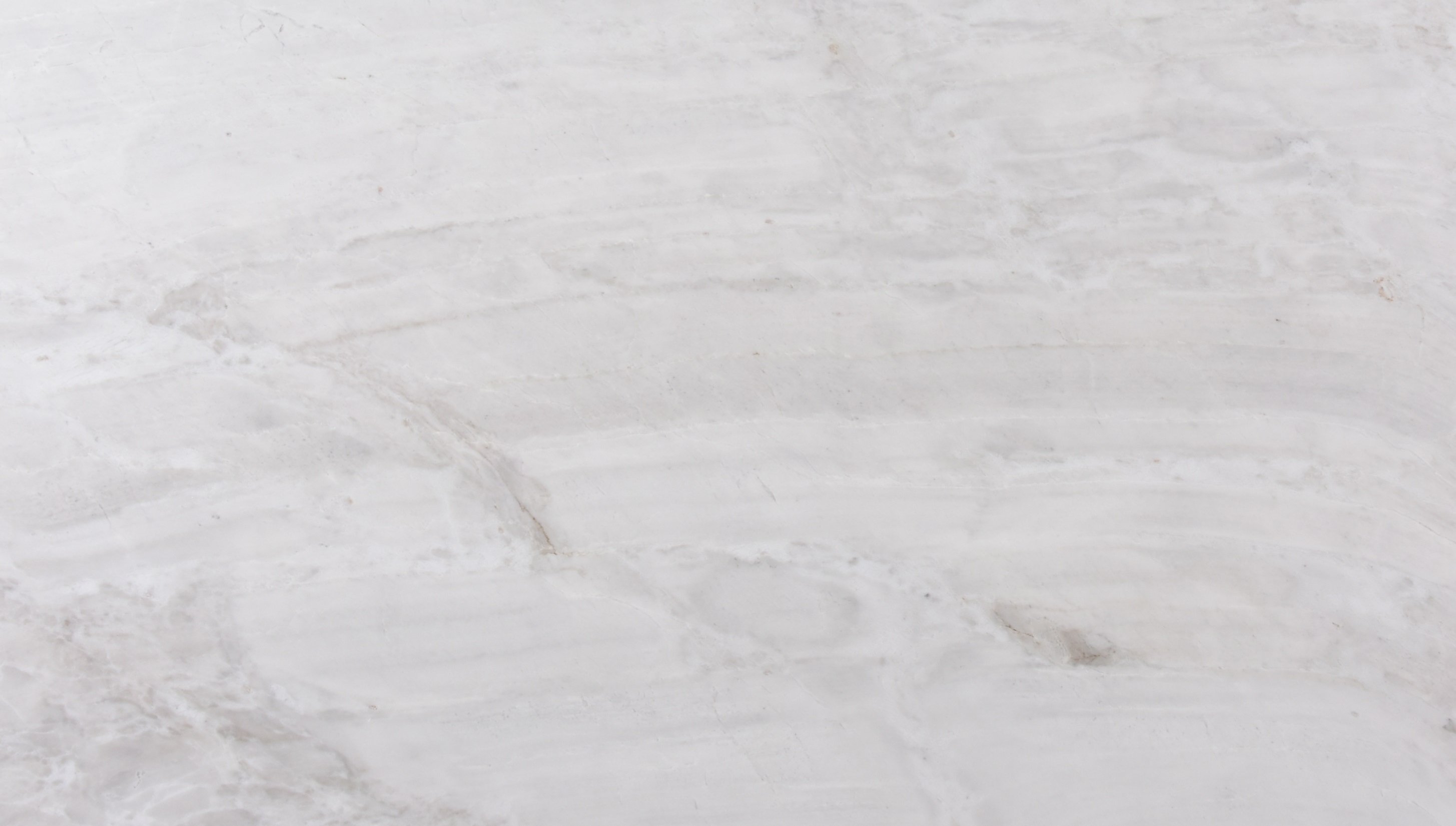
Honed
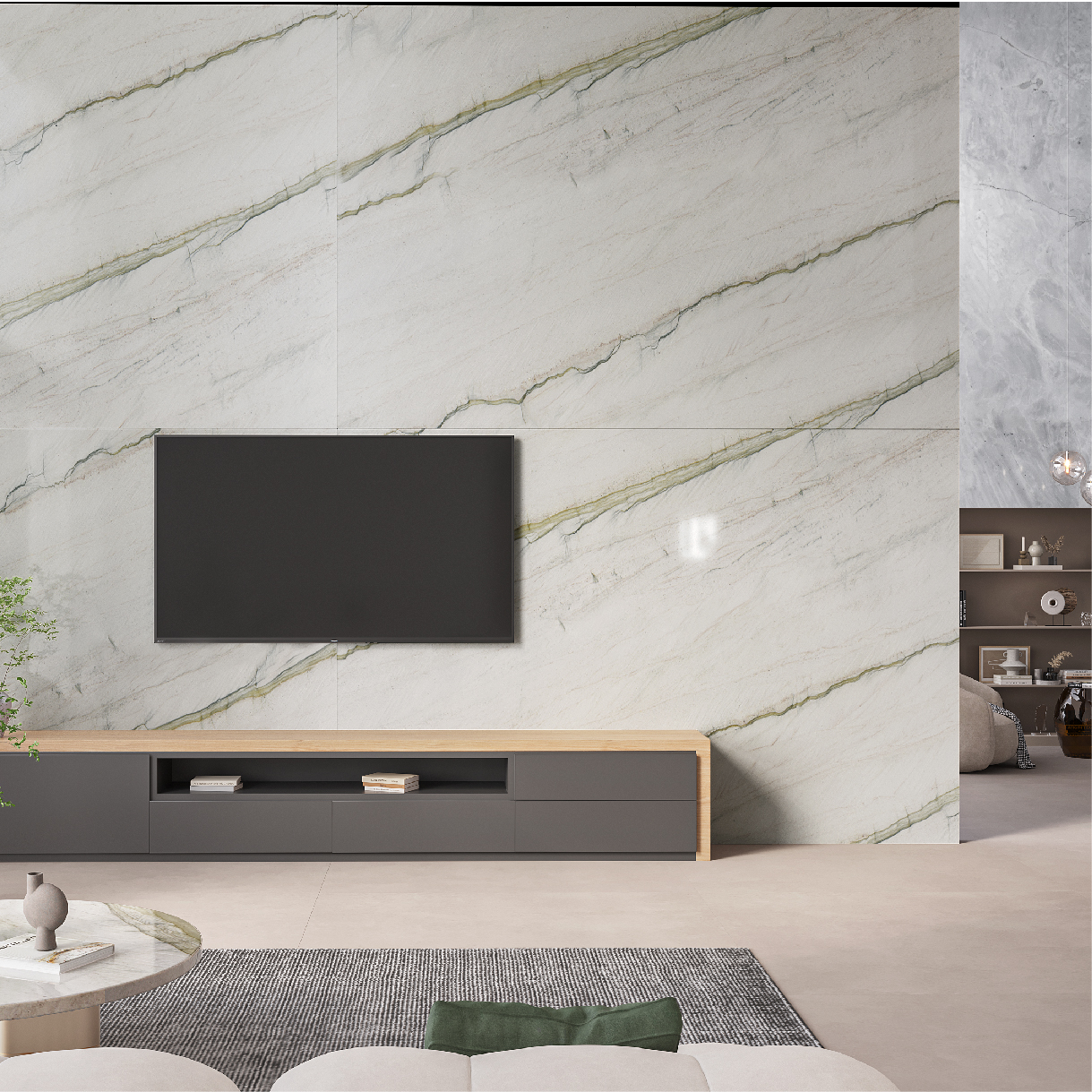
Applications

Quartzites
Quartzito Quartzo (81%), Muscovita (8%), Feldspato (5%), Dumortierita (4%), Rutilo (2%), Turmalina e Zircão (traço)
2655
0.38
0.14
49.67
19.73
167.87
Petrographic Analysis
It consists of classifying the rock through the macroscopic and microscopic description of its characteristics, such as minerological composition, alteration, deformation and microcracking pattern.

Apparently density
Relationship between the mass and apparent volume of the rock. It provides the weight of the rock, being an important parameter for calculating loads in buildings.
Apparent porosity
It is the relationship between the volume of voids and the total volume of the rock expressed as a percentage.

Water absorption
It is the ability to assimilate or incorporate water into the rock, expressed as a percentage.
Abrasion resistance
Determines the wear rate due to friction of particles with the surface of a rock plate.

Bending resistance
Simulates flexural efforts in rock pacas, with predetermined thickness, in this case simulating the effect of wind on plates fixed to facades with metal anchors.
Compressive strength
.
Stain resistance
Stress that causes rock to rupture when subjected to compressive stress.
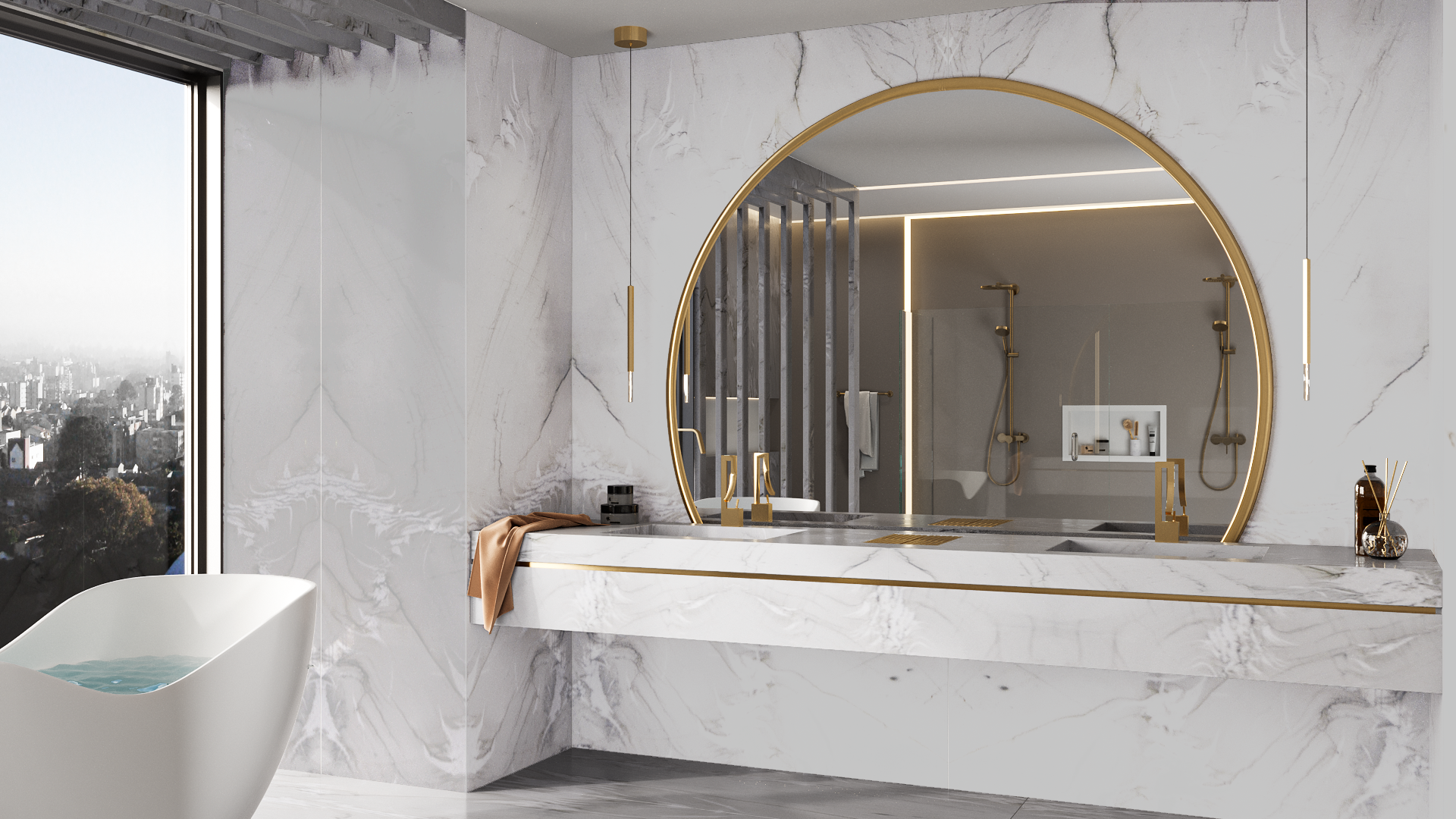
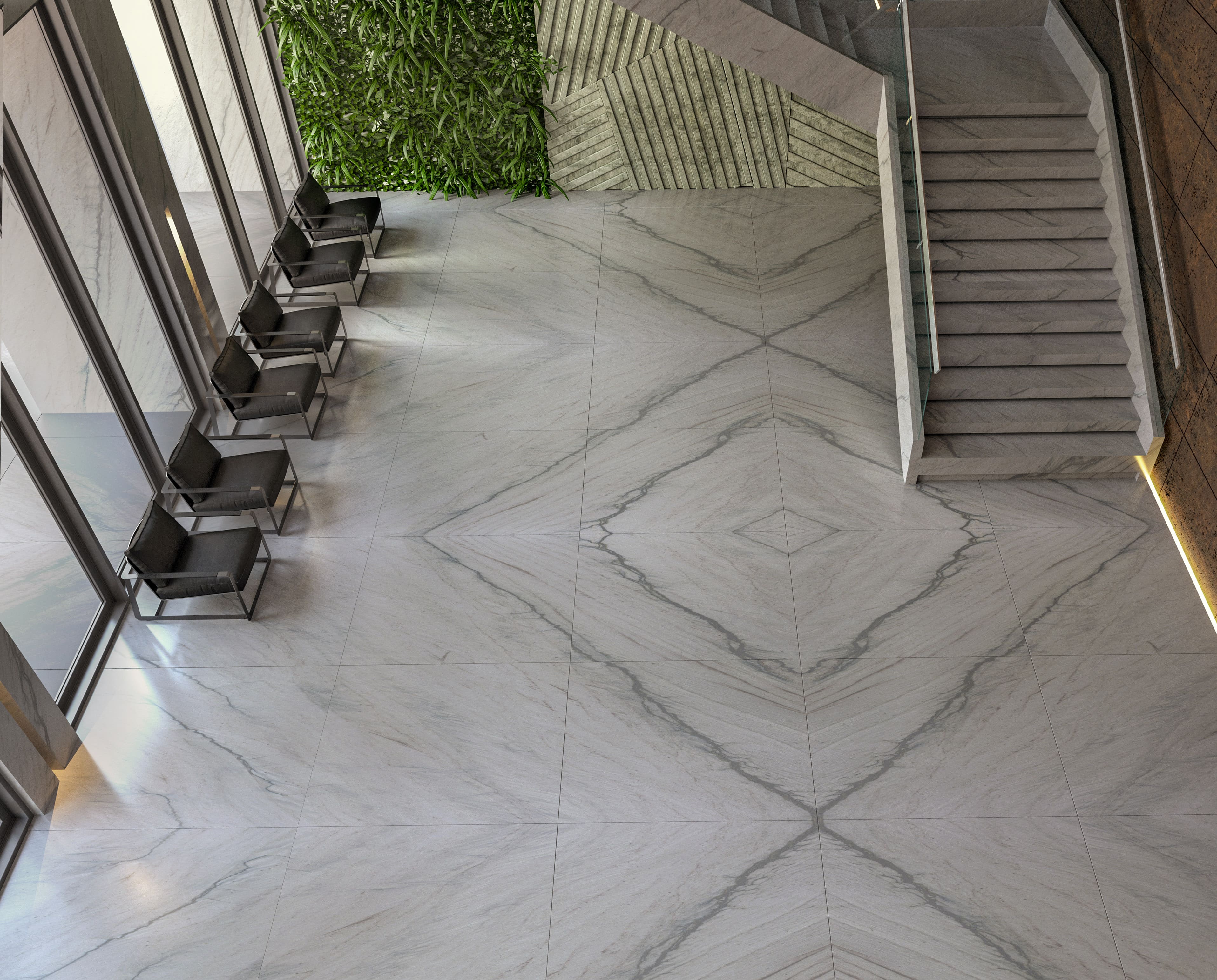
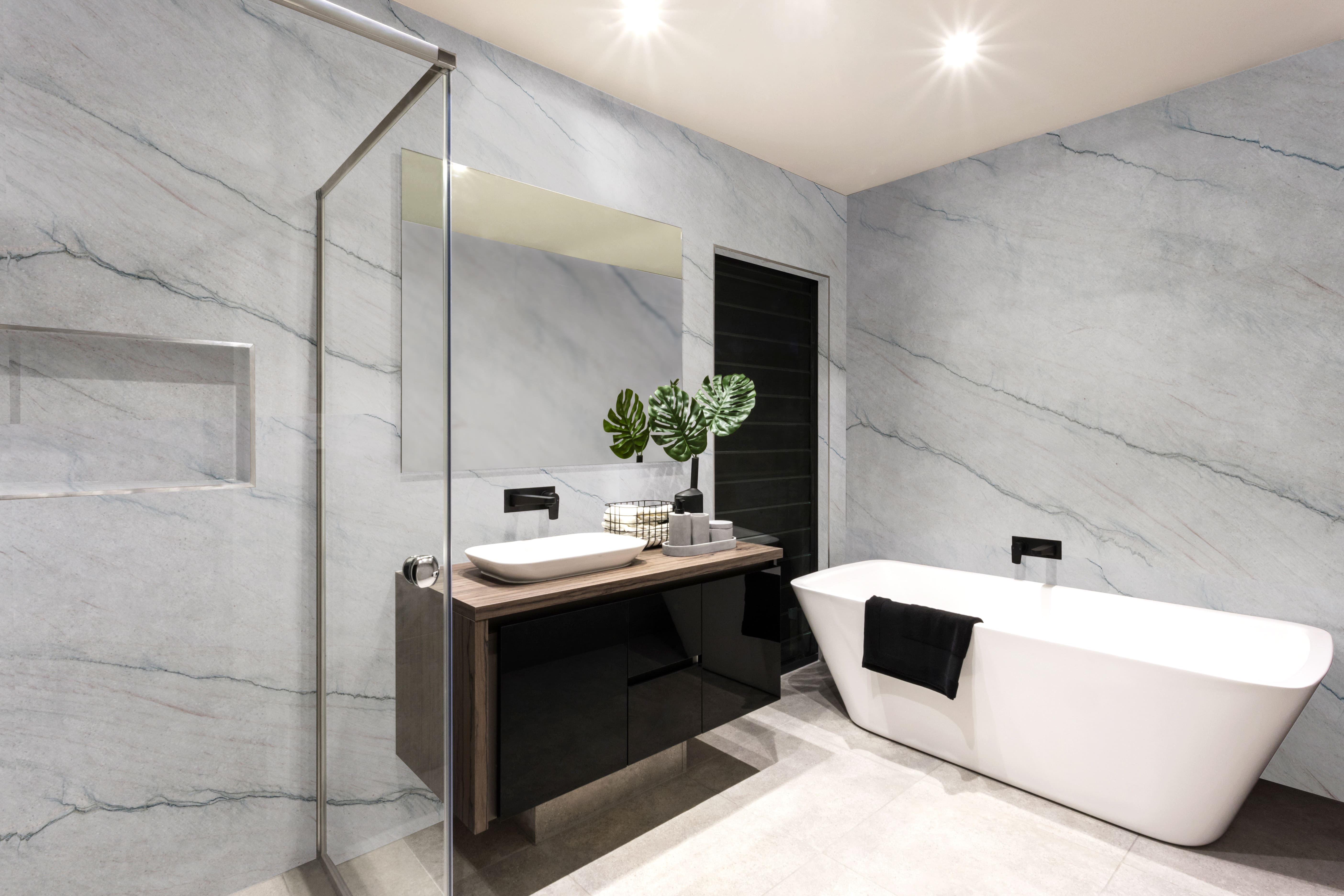
Inspirations
Environments
The exclusive world of natural stones for subtle and elegant environments.
Simulate our products